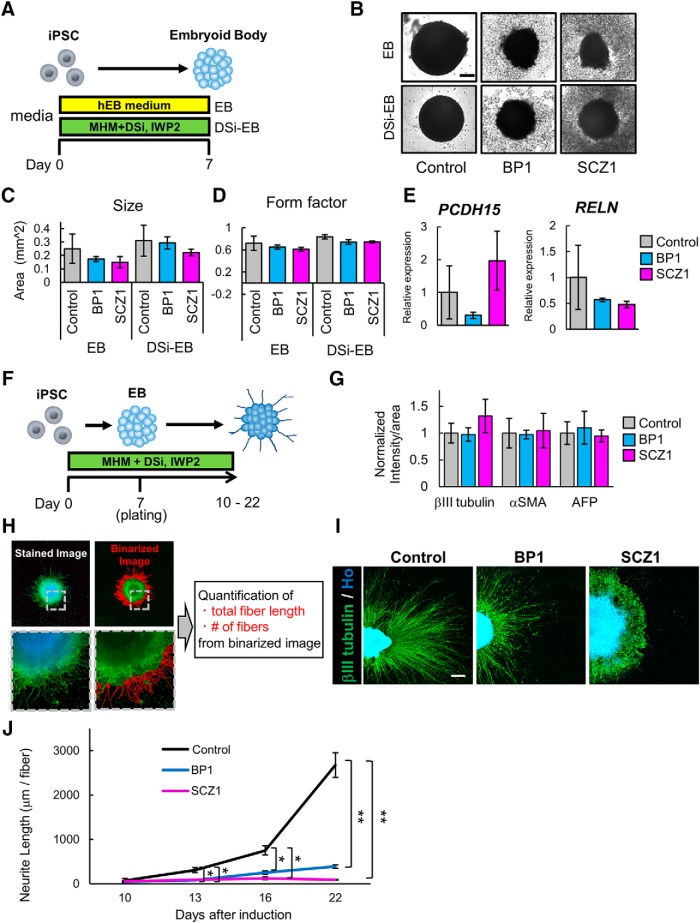
Figure 2.
Neuron differentiation via EB formation. A, Overview of the protocol for EB formation. DSi represents SB431542 and LDN193189. B, Representative images of EBs on day 7. Scale bar, 200 μm. C, Quantification of EB sizes (n = 3 independent experiments; mean ± SD; Dunnett’s test, no significant differences were observed). D, The form factor of the EBs was calculated as an indicator of roundness. E, Gene expression of iPSCs and DSi-EBs. E, Relative gene expression levels of PCDH15 and RELN in DSi-EBs derived from six control lines, two BP lines (BP1-1 and BP1-2), and two SCZ lines (SCZ1-1 and SCZ1-2; n = 3 independent experiments; mean ± SD; Dunnett’s test). Values were normalized to that of the control, which was considered to be 1.0. One sample of 1210B2-derived DSi-EBs, in which PCDH15 expression was under the detection limit, was removed from the analysis. F, Overview of the protocol for neuron differentiation via EB formation. DSi represents SB431542 and LDN193189. G, Intensity levels of three germ layer markers, namely, βIII-tubulin, αSMA, and AFP. Intensity levels were normalized to that of the control, which was considered to be 1.0 (n = 3 independent experiments; mean ± SD; Dunnett’s test among each group, no significant differences were observed). H, Schematic diagram of the analysis protocol. Fiber length and number of βIII tubulin+ cells were quantified from binarized image data obtained from stained images. I, Representative images of βIII-tubulin+ neurons. Scale bar, 300 μm. J, Time-dependent changes of βIII-tubulin+ mean neurite length per neurite fiber (n = 3 independent experiments; mean ± SD; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; Dunnett’s test among each group). Mean neurite length is shown as the mean length of βIII-tubulin+ neurite fiber.