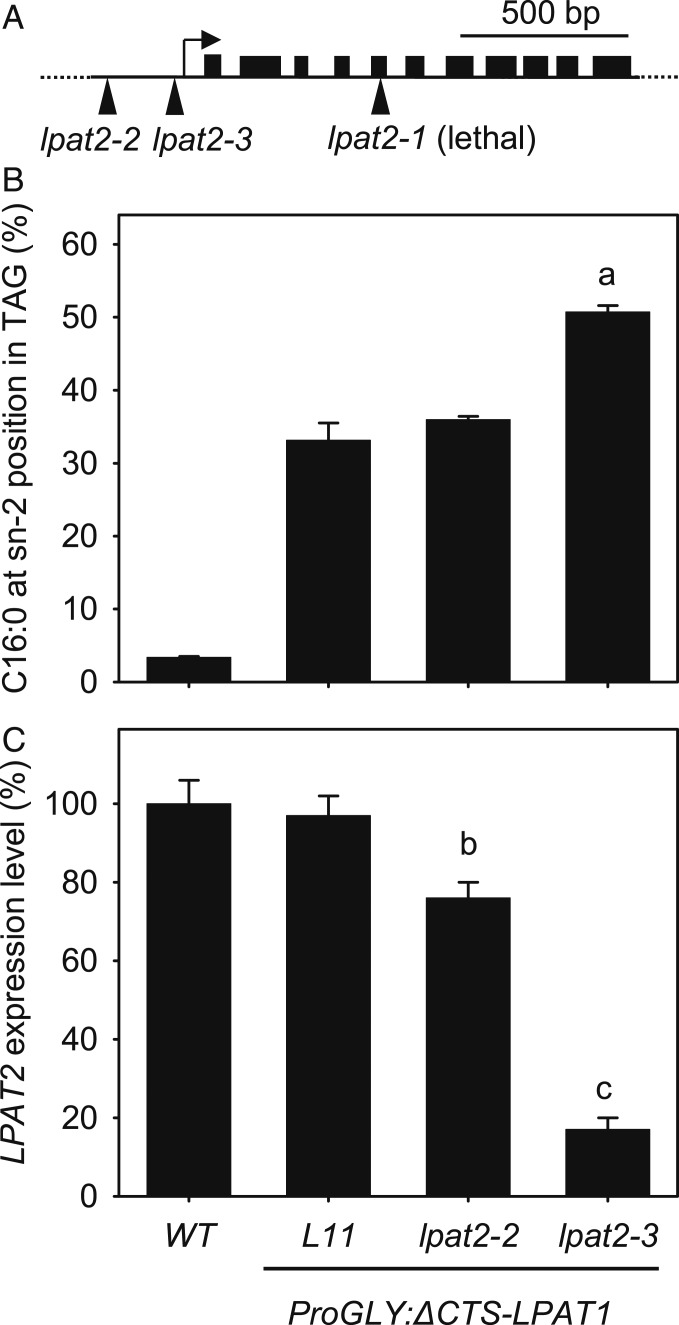
Fig. 3.
Disruption of ER-resident LPAT2 increases C16:0 incorporation into the sn-2 position of TAG. (A) Diagram of LPAT2 locus showing positions of T-DNA insertions in mutant alleles. Effect of lpat2 mutant backgrounds on (B) the percentage of C16:0 esterified to the sn-2 position of TAG, verses sn-1+3, and (C) LPAT2 transcript abundance in seeds expressing ∆CTS-LPAT1. WT, wild type; L11, homozygous ProGLY:∆CTS-LPAT1 line. Values are the mean ± SE of measurements made on separate batches of dry seeds in B and developing siliques in C from 3 plants of each genotype (n = 3). LPAT2 expression was normalized to the geometric mean of 3 reference genes and expressed relative to WT. a, b, and c denote values significantly (P < 0.05) different from L11 (ANOVA + Tukey HSD test).