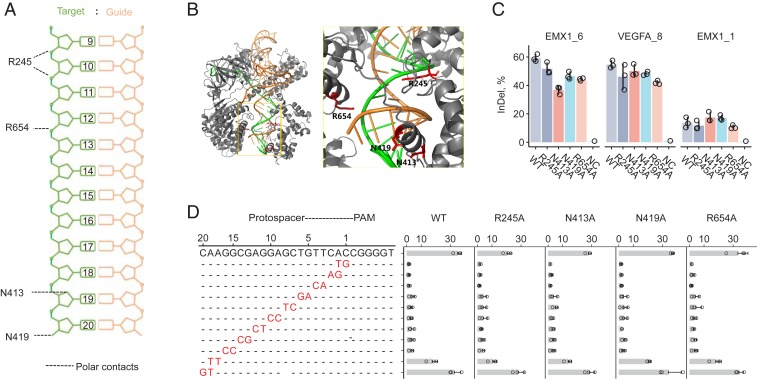
Fig. 1.
Identification and characterization of SaCas9 variants possessing single amino acid substitution at residues forming polar contacts with target DNA. (A) Schematic depicting SaCas9 residues in contact with the target DNA–guide RNA heteroduplex, labeled with protospacer positions (20 being most proximal to PAM). (B) Crystal structure of WT-SaCas9 interacting with the guide RNA–target DNA heteroduplex; close up of the active site showing those residues (red) forming polar contacts within 3.0-Å distance from the target DNA strand (green). (C) Percentage of InDel reads among all amplicon reads of targeted deep sequencing 3 human endogenous sites in HEK293T cells using WT, single mutant variants, and a no-Cas9 negative control (NC). (D) Fluorescence reduction of EGFP cells after gene editing by different SaCas9s using protospacer matched or mismatched sgRNAs (mean ± SD; n = 3).