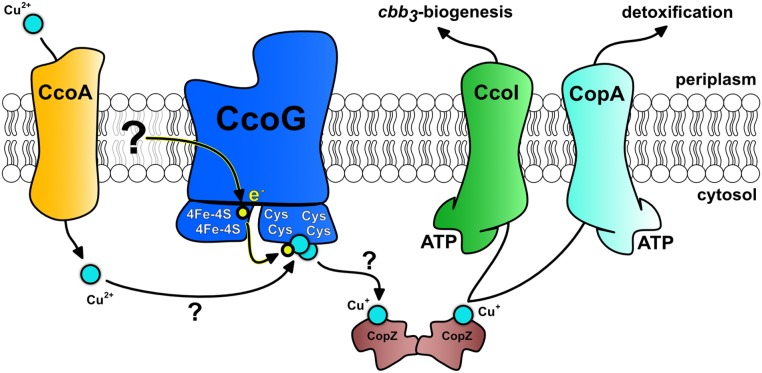
Fig. 7.
Working model for the role of CcoG in cbb3-Cox assembly and Cu homeostasis in R. capsulatus. The model depicts the Cu(II) imported by the MFS-type Cu importer CcoA, which is reduced to Cu(I) by CcoG via its [4Fe-4S] clusters and loaded onto CopZ, conveying it to CcoI for cbb3-Cox biogenesis and to CopA to maintain cellular Cu homeostasis. Cu binding and reduction occur at the 2 Cys motifs via the 2 [4Fe-4S] clusters. The electron donor to CcoG is not known, although the membrane quinone/quinol pool might be a possibility. Arrows with ? indicate the steps that are not yet established experimentally. Accordingly, transient interactions between the components are sufficient for Cu trafficking along the membrane, although some components might form stable complexes.