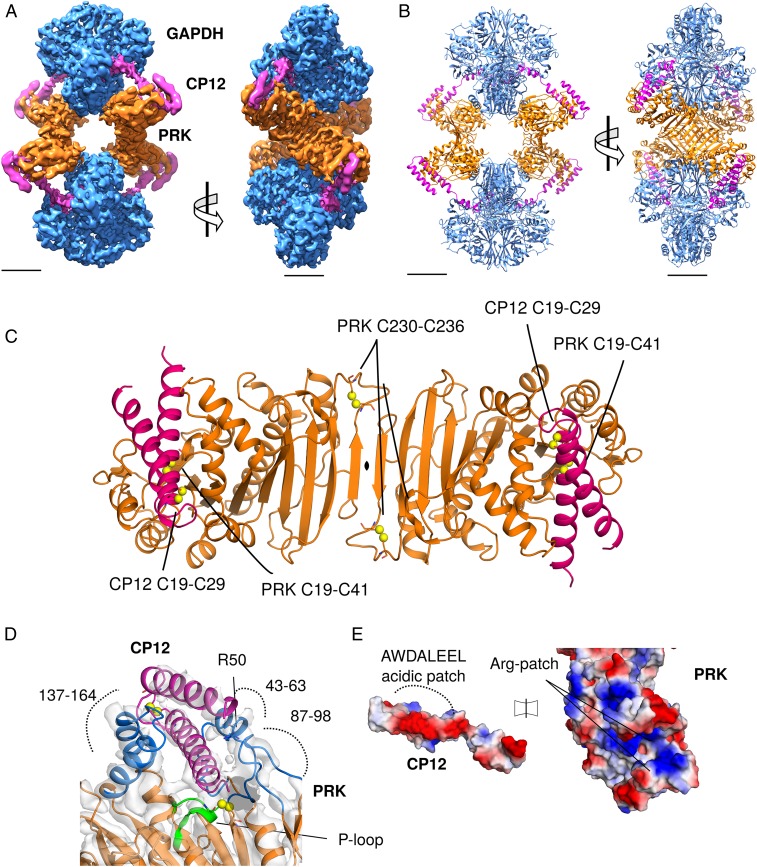
Fig. 3.
CryoEM reconstruction of GAPDH-CP12-PRK complex. (A) CryoEM maps of the complex with GAPDH (blue), PRK (orange), and CP12 (pink), (Scale bar, 30 Å.) (B) Cartoon view of the complex with 2 GAPDH tetramers and 2 PRK dimers forming an elongated diamond-shaped complex tethered by 4 CP12 chains. (C) Cartoon view of PRK dimer, with CP12 bound in the 2 active sites; disulfides in both proteins labeled. (D) CP12 (pink) sterically blocks PRK (orange) by binding in the active site (blue). The PRK active site cleft is formed of regions 147–164, 43–63, and 87–98. The PRK ATP-binding P-loop region (green) and Arg50 are indicated. (E) Electrostatic surface potential of CP12 and PRK interface regions, showing charge complementary. The CP12 conserved AWDA(V/L)EEL motif is highlighted.