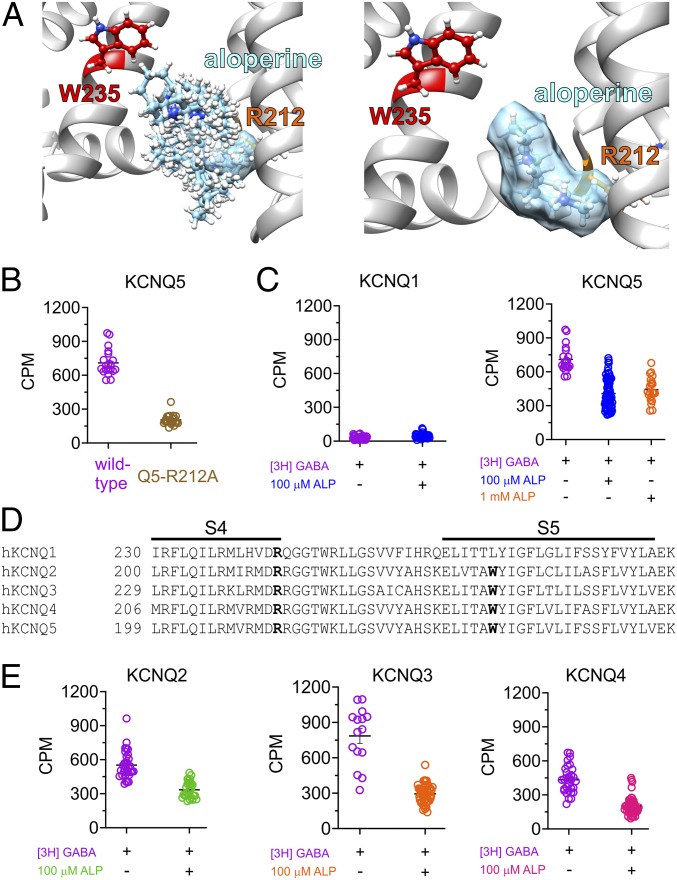
Fig. 7.
Aloperine KCNQ isoform selectivity is independent of binding selectivity. All error bars indicate SEM. (A, Left) Superimposition of all of the aloperine binding poses in the neurotransmitter binding pocket of KCNQ5 predicted by SwissDock. (A, Right) Aloperine spacefill model in the central binding pose of all of the superimposed binding poses (Left). (B) Comparison of tritiated GABA binding (for these and all following panels, bound GABA activity is expressed in counts per minute [cpm] to wild-type and R212A KCNQ5 expressed in oocytes; n = 20 to 22). (C) Effects of aloperine on tritiated GABA binding to KCNQ5 (n = 20 to 74); KCNQ1 (n = 37 to 41) was used as a negative control for GABA binding. (D) Amino acid sequence alignment of the S4 to S5 regions of human KCNQ1–5. KCNQ5-R212 and KCNQ5-W235 (and equivalents) are shown in bold. (E) Effects of aloperine on tritiated GABA binding to KCNQ2 (n = 33 to 57), KCNQ3 (n = 15 to 48), and KCNQ4 (n = 31 to 55).