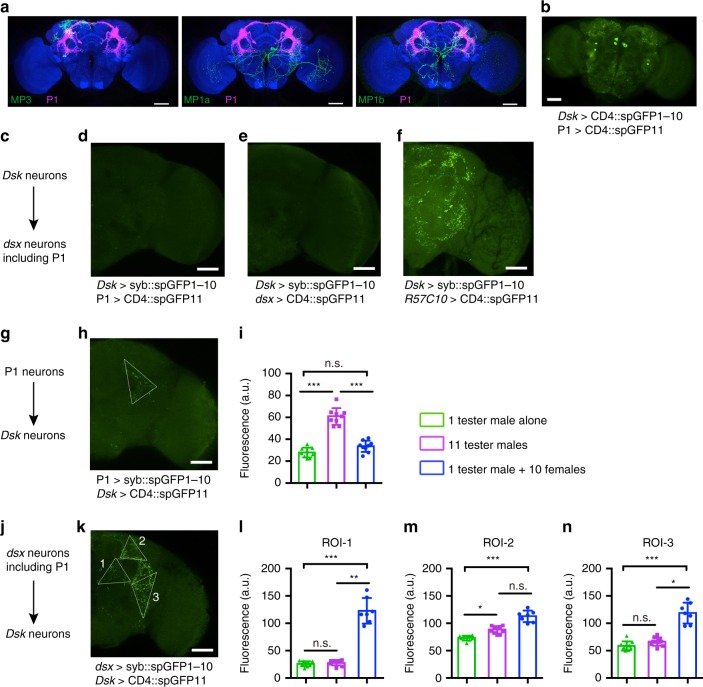
Fig. 5.
Experience-dependent synaptic interaction between Dsk and P1 neurons. a Registration of P1 neurons and Dsk MP neurons in a standard brain. b Potential membrane contacts between P1 and Dsk neurons as revealed by conventional GRASP technique. Representative of five male brains. c–f There is no syb-GRASP signal from Dsk neurons to dsx neurons including P1 neurons. Representative of five male brains for each genotype. g–i Experience-dependent synaptic transmission from P1 neurons to Dsk neurons as revealed by syb-GRASP signals. n = 9 for each. p < 0.001, One-way ANOVA. ***p < 0.001, post hoc Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. j–n Experience-dependent synaptic transmission from dsx neurons (including P1 neurons) to Dsk neurons as revealed by syb-GRASP signals in single-housed males (green bar) and group housed males (magenta bar for male–male group, and blue bar for male–female group). n = 10, 10 and 7 for each group respectively. For ROI-1: p < 0.001, Kruskal–Wallis test. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and p > 0.99 (n.s.), post hoc Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. For ROI-2: p < 0.001, Kruskal–Wallis test. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 and p = 0.08 (n.s.), post hoc Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. For ROI-3: p < 0.001, Kruskal–Wallis test. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 and p = 0.31 (n.s.), post hoc Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. n.s. not significant. Error bars indicate SEM. Source data are provided as a Source Data file