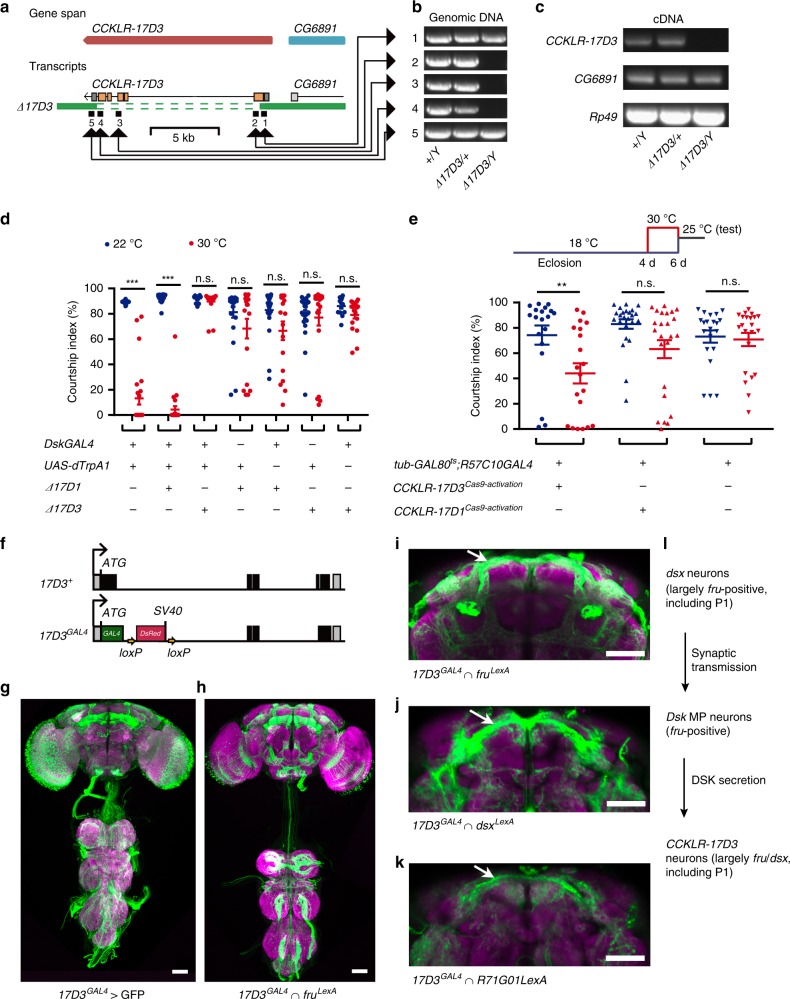
Fig. 7.
CCKLR-17D3 inhibits male courtship. a–c Generation and validation of a 9.04 kb deletion mutant of the CCKLR-17D3 gene. d Courtship inhibition by activating DskGAL4 neurons is dependent on DSK’s receptor CCKLR-17D3 but not CCKLR-17D1, as mutation in CCKLR-17D3 but not in CCKLR-17D1 restores courtship by DskGAL4/UAS-dTrpA1 males at 30 °C. Genotypes as indicated. n = 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 18, 24, 18, 24, 24, 24, 18, and 13, respectively. ***p < 0.001, Mann–Whitney U test. e Acutely over expression of CCKLR-17D3 but not CCKLR-17D1 two days before courtship test significantly suppresses male courtship. n = 19, 20, 24, 24, 21, and 22 respectively. p < 0.01, Kruskal–Wallis test. **p < 0.01 and p > 0.1 (n.s.), post hoc Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. n.s. not significant. Error bars indicate SEM. f Generation of knock-in GAL4 into the CCKLR-17D3 locus. g Expression pattern of 17D3GAL4 visualized by UAS-myrGFP in male CNS. Representative of eight males. h, i Intersectional expression between 17D3GAL4 and fruLexA in the male CNS. Representative of five males. Arrow indicates the male-specific P1 neurons (i). Genotype: 17D3GAL4/Y; UAS > stop > myrGFP LexAop2-FlpL/+; fruLexA/+. j, k Intersectional expression between 17D3GAL4 and dsxLexA (j), 17D3GAL4 and R71G01LexA (k) in males. Representative of five males each. Arrow indicates the male-specific P1 neurons. Scale bars, 50 μm. l An illustration from dsx neurons acting on Dsk neurons via synaptic transmission, and Dsk neurons to CCKLR-17D3 neurons via secretion of DSK. Source data are provided as a Source Data file