FIGURE 1.
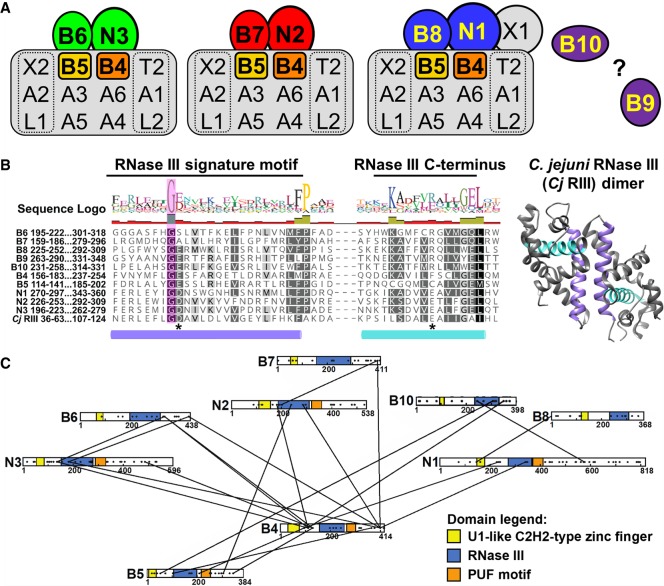
RNase III domains have been identified in several editosome proteins. (A) Schematics of KREN1, KREN2, and KREN3 editosomes, with proteins containing an RNase III domain highlighted in color. Nonessential KREPB9 and KREPB10 are shown apart as they variably associate with editosomes. Editosomes contain 12 common core proteins, while KREN1, KREN2, and KREN3 and their partner proteins are mutually exclusive. (B) Alignment of RNase III domain sequences from KREPB4-B10, KREN1-N3, and C. jejuni (accession Q9PM40). A total of 299 sequences from 35 kinetoplastid species and strains were aligned using MUSCLE. Only T. brucei sequences and the RNase III signature motif/C-terminus are shown here for clarity. Colored cylinders denote the α-helices shown colored in the C. jejuni RNase III dimer structure (PDB ID 3O2R). A universally conserved glycine residue in the RNase III signature motif is shown shaded in magenta. Asterisks denote residues that are universally conserved in catalytic RNase IIIs, equivalent to D44 and E116 in C. jejuni. (C) Schematic showing location of crosslinks between RNase III domain containing editosome proteins identified in CXMS (McDermott et al. 2016). Domains are highlighted as indicated based on bioinformatics predictions (Worthey et al. 2003; Carnes et al. 2012b; McDermott et al. 2016). Black dots distributed across proteins indicate the positions of lysine residues available for CXMS crosslinking (McDermott et al. 2016).