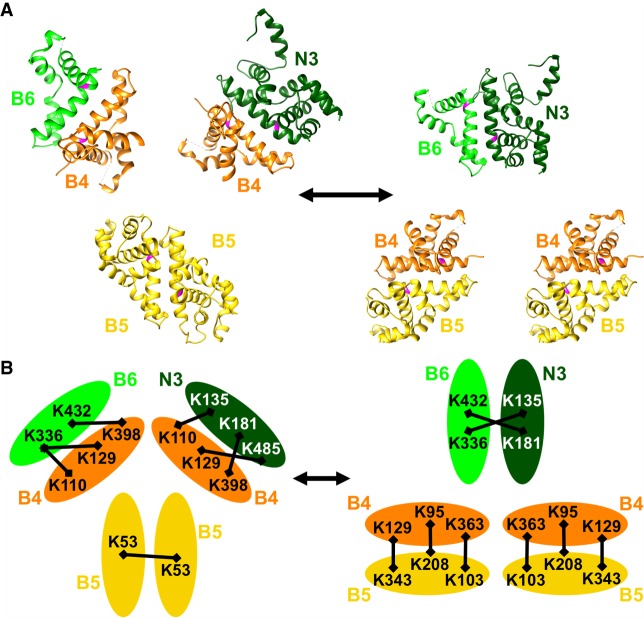
FIGURE 7.
Proposed model for RNase III interactions within editosomes. Top panel (A) shows RNase III domain structures modeled on C. jejuni 3O2R for KREPB4 (orange), KREPB5 (yellow), KREPB6 (light green), and on 1O0W for KREN3 (dark green) (McDermott et al. 2016) in two configurations: On the left, two KREPB5 domains dimerize while KREPB4 forms dimers with KREPB6 and KREN3; and on the right, two dimers of KREPB4 with KREPB5 form while KREPB6 and KREN3 dimerize. Universally conserved glycine residue critical for function shown in magenta in each domain. Interchange between these configurations could facilitate ES recognition and cleavage by KREN3 using enzyme–pseudoenzyme regulation of catalytic activity. Bottom panel (B) shows crosslinks identified by CXMS between KREPB4, KREPB5, KREPB6, and KREN3 (represented by ovals), all of which are consistent with configurations in the model shown in the top panel (McDermott et al. 2016). Crosslinked Lys residues (K) are indicated by their position in the protein, and crosslinks depicted by black bars. Similar configurations are proposed for KREPB7-KREN2 and KREPB8-KREN1 but are not shown.