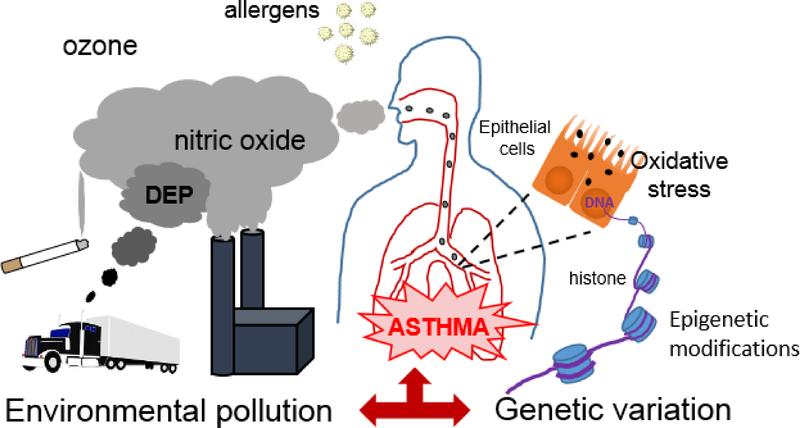
Figure 1.
Summary of the processes leading to gene-air pollution interaction effects in asthma. Inhaled particulate and gaseous components and allergens activate inflammatory and oxidative stress-related pathways in the airways. Genetic variation may result in allele-specific air pollution-related epigenetic modifications of genes involved in the development of asthma.