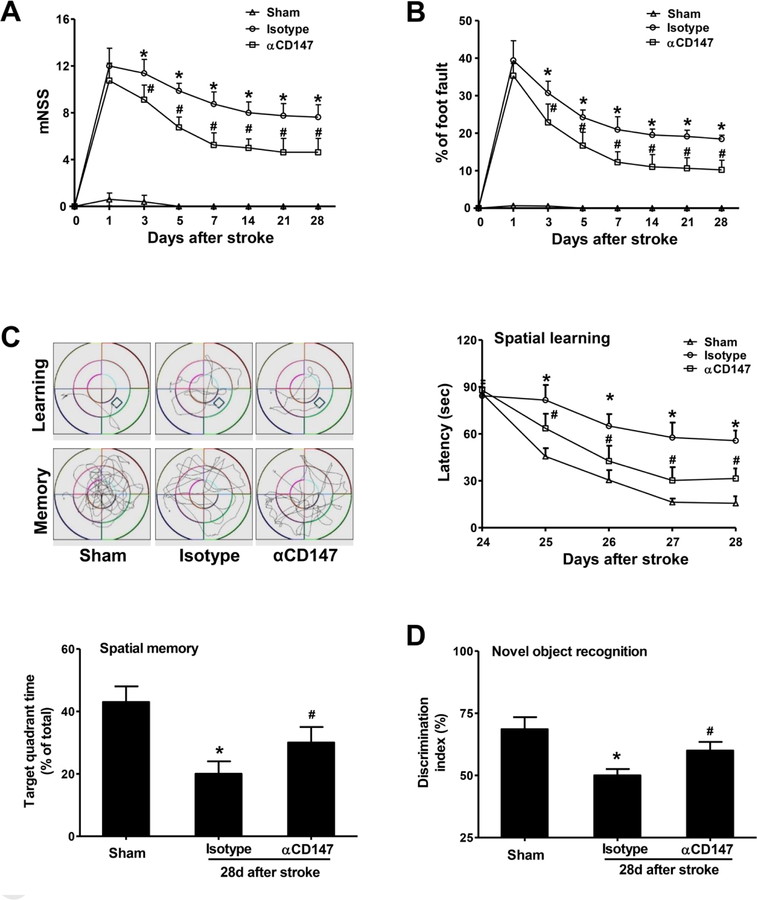
Figure 2.
Inhibition of CD147 improves sensorimotor and cognitive functions 28 days after stroke. All behavioral tests were performed on the same mice used in Figure 1. A and B, The modified neurological severity score (mNSS) test (A) and foot-fault test (B) measured before (day 0) and up to 28 days after stroke, n=7–14 mice per group. C, The Morris water maze test was performed to measure cognitive deficits, n=7–14 mice per group. (upper, left panel) Representative images showing swim paths of mice during the learning and memory tests. (upper, right panel) Latency to locate the hidden platform in the cued learning test from 24 to 28 days after stroke. (lower, left panel) Spatial memory, defined as the percentage of time spent in the target quadrant after the platform was removed, was measured at 28 d after stroke. D, Novel objective recognition (NOR) was measured on day 28 after stroke, n=7–14 mice per group. Discrimination index=time spent exploring novel object / (time exploring novel object + time exploring familiar object) x 100%. *p < 0.05 vs. Sham; #p < 0.05 vs. Isotype.