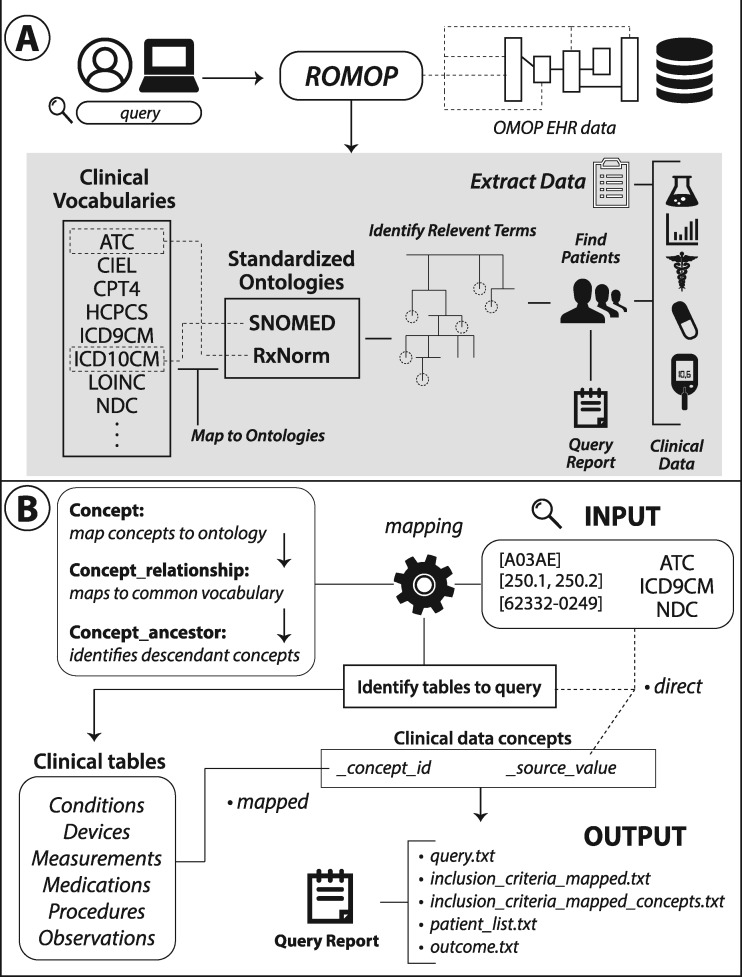
Figure 1.
Schematic and structure of ROMOP. (A) ROMOP interfaces with OMOP-formatted EHR data in a relational database structure. Users can retrieve all relevant clinical, demographic, and encounter data for a list of patients directly into an R object as well as search for patients using any vocabulary contained within the OMOP CDM. (B) When searching for patients using clinical vocabularies, ROMOP offers the option to automatically map (“map” option) to the standardized ontology (eg, SNOMED) and query all concepts lower in the hierarchy (ie, descendants). Alternatively users can search for terms directly (“direct” option). ROMOP identifies the relevant clinical tables and fields to query and can produce a set of outputs detailing the query and outcomes. CDM: common data model; EHR: electronic health record; OMOP: Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership.