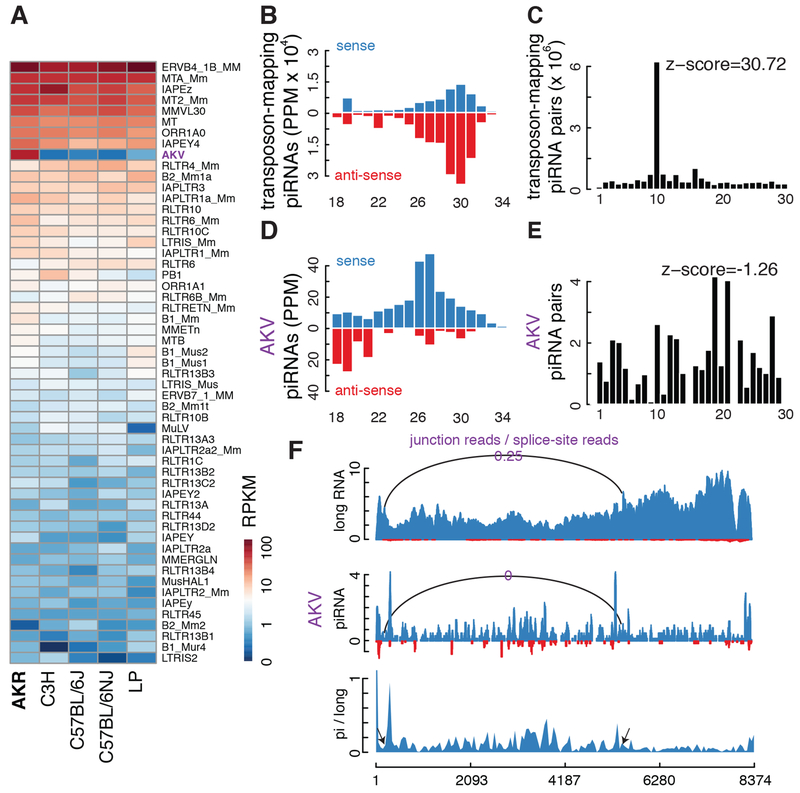
Figure 5. piRNA production from AKV murine leukemia virus.
A. Heatmap depicting expression of transposon subfamilies in testis from five mouse strains: AKR, C3H, C57BL/6J, C57BL/6NJ and LP. Only transposon families with expression levels higher than 1 RPKM are shown. AKV, which is marked in purple, is only over-expressed in AKR mice. B. Histogram summarizing size and strand abundance for small RNAs targeting all transposons in AKR testis. C. Frequency of overlap between sense and antisense transposon-targeting piRNAs in the AKR mouse testis. D. Histogram showing size and strand bias for piRNAs targeting AKV.E. Frequency of sense-antisense overlap for AKV piRNAs, which does not support ping-pong. F. Normalized long RNA and piRNA reads across AKV, with sense reads in blue and antisense reads in red. The ratios of junction to splice site reads for the main intron are indicated: 25% of long RNAs are spliced, but no piRNA reads mapped to the exon-exon junction. The bottom track plots the ratio of piRNAs to long RNAs and is elevated over the intron.