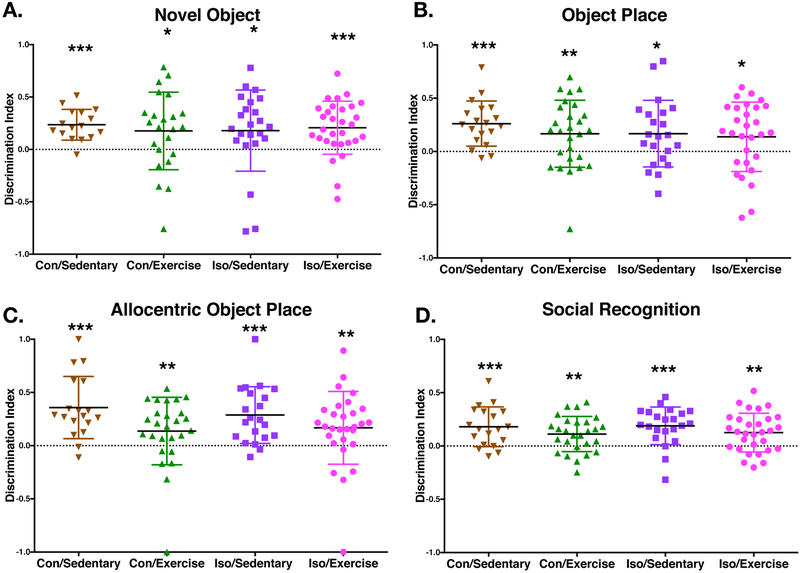
Figure 3. Recognition memory preserved after early life isoflurane exposure.
A–C. Recognition memory tasks testing specific domains of recognition memory with increasing difficulty from Novel Object Recognition, Object Place Recognition to Allocentric Object Place Recognition (Con/Sedentary n=16, Con/Exercise n=23, Iso/Sedentary n=23, Iso/Exercise n=30). Displayed is the discrimination index for individual animals which is the time spent investigating the goal object minus the time investigating the non-goal object, divided by the total time exploring both objects. A two-way non-parametric test (Wilcoxon Signed Rank) was performed for each group which found a significant difference from chance (zero) for all groups in the three variations of recognition memory tested. D. Social recognition was tested with juvenile male rats as targets. Like the other recognition tasks, all groups had a significant difference from chance (Wilcoxon Signed Rank). Solid bar represents mean value. Error bars represent standard deviation. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001