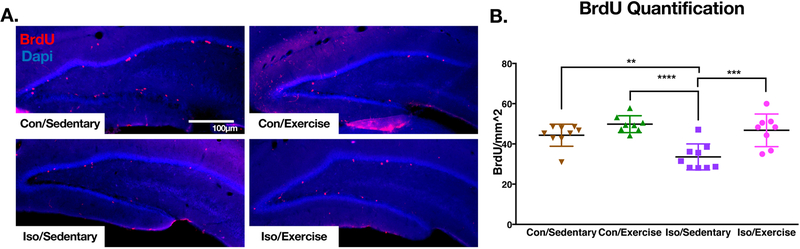
Figure 5. BrdU labelling at P43 in perinatally isoflurane exposed animals is decreased in sedentary animals but is increased with exercise.
A. Representative immunohistochemistry processed images from the hippocampus of P43 animals after a 3hr. BrdU pulse. B. Quantification reveals significant differences between Iso/Sedentary animals and every other group by Tukey’s multiple comparisons suggesting early life isoflurane exposure reduces proliferating cells in the hippocampus, but can be reversed with exercise in adulthood (p values adjusted for multiple comparisons). (Con/Sedentary n=8, Con/Exercise n=9, Iso/Sedentary n=8, Iso/Exercise n=9). Solid bars represent mean and error bars represent standard deviation. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001