Fig. 2.
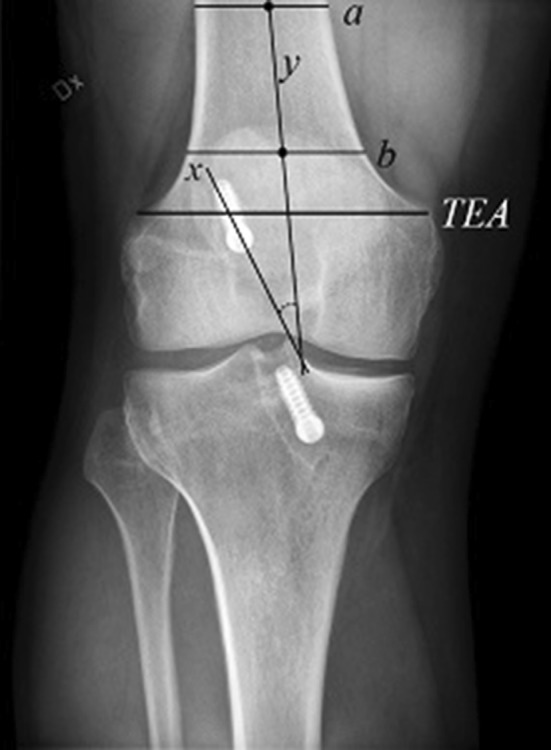
A radiograph showing the method used to measure the femoral tunnel angle formed by the femoral tunnel and the long axis of the femur in posteroanterior radiographs. The most proximal portion of the femoral epicondyle was bisected by a line forming the transepicondylar axis (TEA). At the most proximal part of the femur, visualized on the radiograph, a line was drawn along the width of the diaphysis and parallel to the TEA (a). Distal to this line, at a distance from line a that corresponds to half the length of the TEA, another parallel line was drawn (b). The midpoint of lines a and b was crossed by a line parallel to the axis of the diaphysis. The femoral tunnel was visualized and a line was drawn through its axis (x). The angle formed between this line and line y was defined as the femoral tunnel angle
