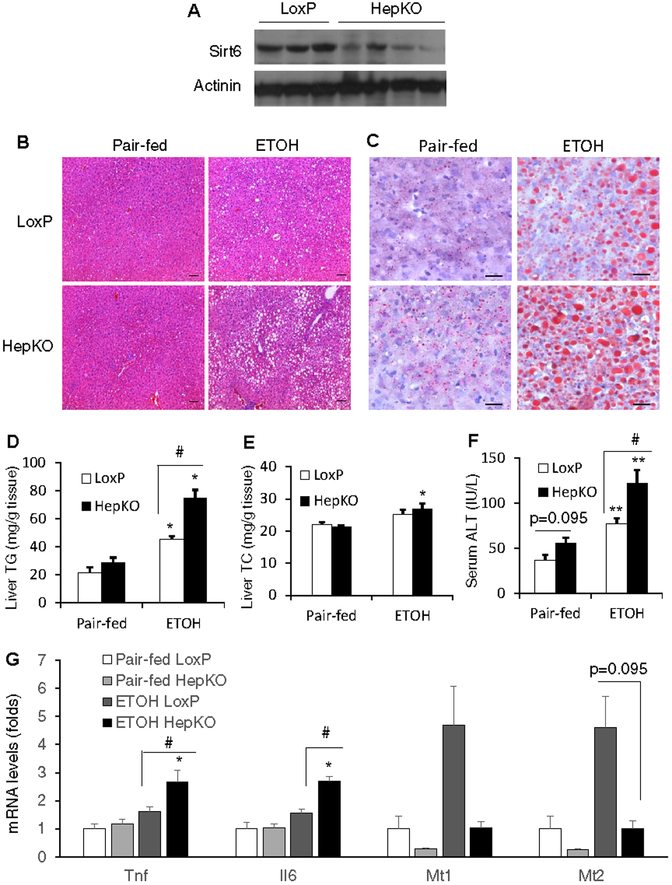
Fig. 3. Hepatocyte-specific Sirt6 knockout (HepKO) mice develop alcoholic liver disease.
Control LoxP and Sirt6 HepKO female mice were pair-fed or ethanol-fed (5% vol/vol) for 10 days plus a single binge (5 g/kg) on day 11. (A) Western blot analysis of Sirt6 in the liver of control LoxP and HepKO mice. (B) Representative H&E stained liver sections (100× magnification). (C) Representative liver sections stained by oil Red O (200× magnification). (D, E) Hepatic TG and TC measurements. (F) Serum ALT measurements. (G) mRNA analysis of Tnf, Il6, Mt1, and Mt2 genes in the liver of control LoxP and HepKO mice. Data are presented as means ± S.E.M. #p < 0.05 for LoxP vs. Sirt6 HepKO; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 for Pair-fed vs. ETOH for the same genotype (n=4–5/group). Scale bars: 50 μm. TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride.