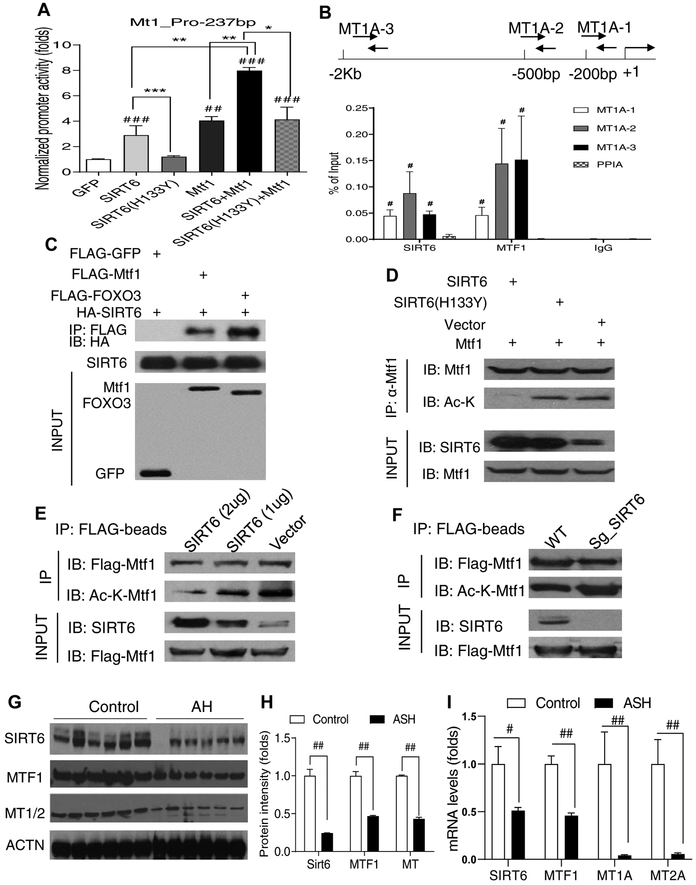
Fig. 8. SIRT6 induces hepatic Mt1 gene expression by interaction and activation of Mtf1.
(A) Mt1 gene promoter activity analysis by transfection of luciferase reporters and GFP, SIRT6, SIRT6 (H133Y), or Mtf1 plasmids in HEK 293T cells (n =6–7/group). (B) ChIP qPCR analysis of the association of SIRT6 and MTF1 with the proximal promoter of the human MT1A gene under the ethanol treatment condition in VL-17A (n =4/group). (C) Co-IP analysis of an interaction between SIRT6 and Mtf1 in HEK 293T cells. (D) Mtf1 deacetylation analysis by cotransfection of Mtf1 and SIRT6 or SIRT6 (H133Y) in VL-17A cells. (E) Dose-dependent Mtf1 deacetylation analysis in VL-17A cells. (F) Mtf1 acetylation analysis in SIRT6-deficient VL-17A cells. (G, H) Western blot and quantification analysis of SIRT6, MTF1, and MT1/2 proteins in the liver of normal controls and AH patients (n=6). (I) qPCR analysis of SIRT6, MTF1, MT1A, and MT2A mRNAs in the liver of normal controls and AH patients (n=6). Data are presented as mean ± S.E.M. In panels A and B: #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, and ###p < 0.001 vs. GFP or PPIA; *p < 0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 for the indicated promoter reporter assays. In panels H and I: #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01 for AH vs. Control. ACTN, actinin; AH, alcoholic hepatitis; ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; Co-IP, co-immunoprecipitation; qPCR, quantitative PCR.