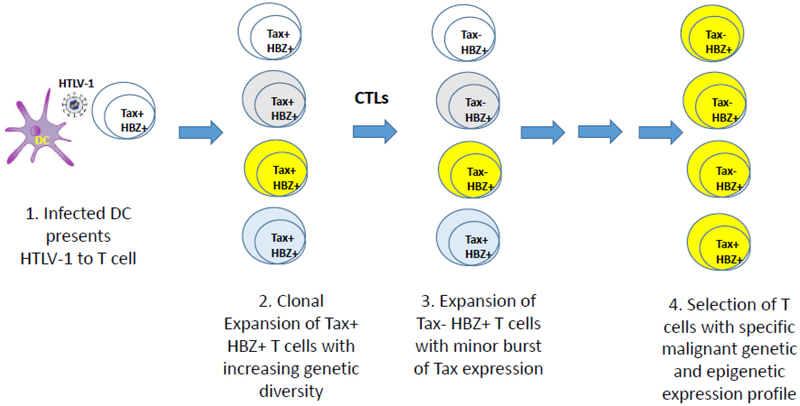
Fig 3.
Multiple Events of HTLV-1 Infection and Transformation. The schematic hypothesizes that the initia HTLV-1 infected cell is a dendritic cell which presents infectious virus to a T cell. Subsequent expression of Tax, HBZ, and plus strand virus genes result in infection and clonal expansion of other T cells, resulting in genetic heterogeneity, as indicated by different colored cells. Immune responses, as well as viral gene restrictions, result in little or no Tax and plus strand gene product expression from the majority of infected T cells, but a minor population of T cells with transient bursts of Tax expression. Several decades of infection result in selection of cells with specific combinations of genetic and epigenetic alterations that result in adult T-cell leukemia lymphoma.