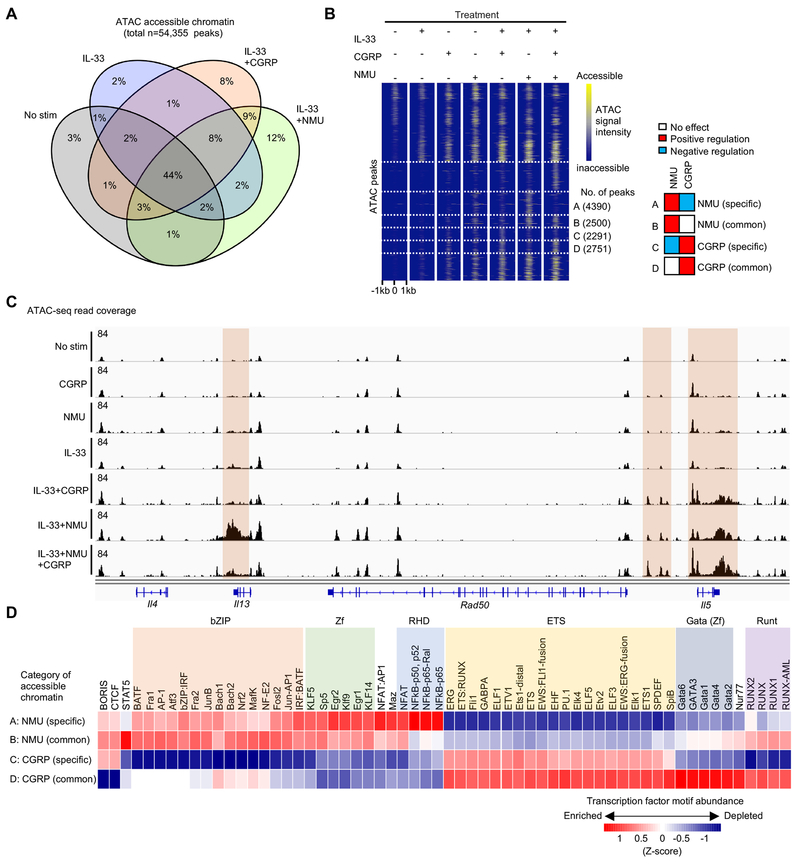
Figure 4. Differential effects of CGRP and NMU on ILC2 regulatory elements.
(A) Venn diagram demonstrating percentages of 54,355 chromatin accessible regions identified by FastATAC-seq among ILC2s treated with or without IL-33, CGRP, and NMU for 4 hr. (B) Heatmap illustrating the chromatin accessibility among the dynamic regions shown in A, highlighting 4 categories of differentially accessible regions. Categories A and B represent NMU targeted regions that are independent (A) of, or antagonized (B) by CGRP, respectively. Categories C and D represent CGRP targeted regions that are independent (C) of or counteracted (D) by NMU, respectively. (C) Genomic track view of Th2 cytokine loci showing distinct regulation of chromatin accessibility of Il5 and Il13 loci across different conditions. (D) Heatmap showing relative enrichment of TF motifs within chromatin regions categorized in B. Data are from representative (C) of two independent experiments with similar results.