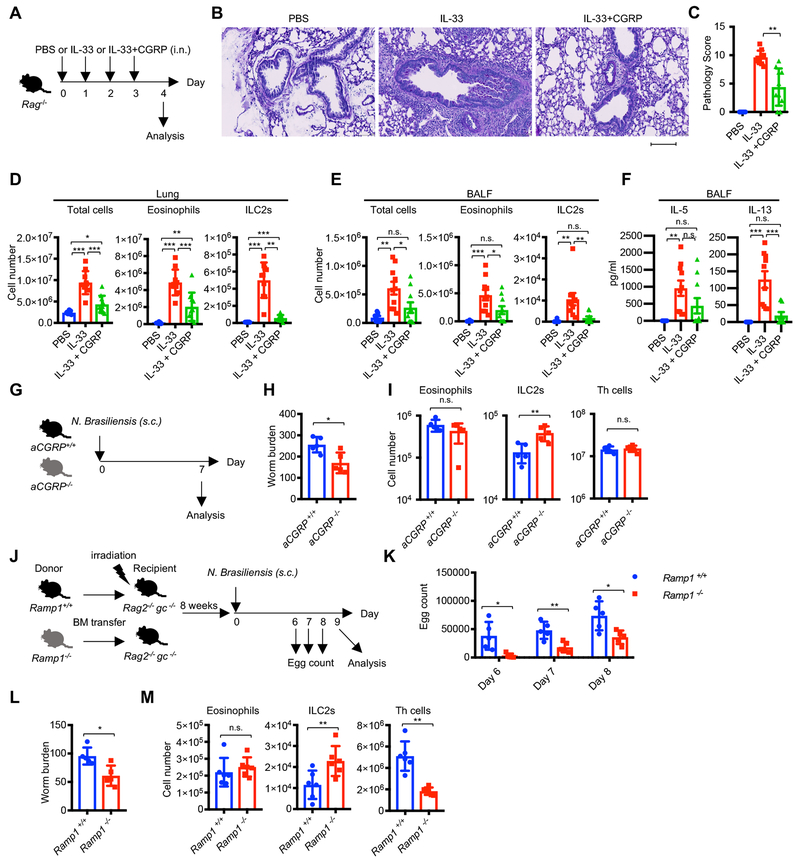
Figure 6. CGRP is required for negatively regulating ILC2s and type 2 responses in vivo.
(A-F) Effect of CGRP in IL-33-induced pulmonary inflammation. (A) Rag1−/− or Rag2−/− mice were administered PBS (n=8), IL-33 (n=10), or IL-33+CGRP (n=10) intranasally for four consecutive days, with the following analyses of lung pathology one day after the last administration: (B) Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining, (C) Pathology score, (D) Cell count of total cells, eosinophils (CD11c− CD11b+ Siglec-F+) and ILC2s (Lin− Thy1+ CD127+ GATA3+), (E and F) Cell counts (E) and cytokine production (F) in BALF. The scale bar in B is 100 μm. (G-I) Impact of genetic deletion of CGRP on helminth infection: Experimental scheme (G) and worm count of small intestine (H) or cell numbers of eosinophils, ILC2s and Th cells (I) in mLNs from aCGRP+/+ (n=5) or aCGRP−/− (n=5) mice infected with N. brasiliensis and analyzed at day 7 post infection. (J-M) Impact of genetic deletion of CGRP receptor subunit Ramp1 in transferred hematopoietic cells following helminth infection-experimental scheme (J). Fecal egg counts (K), small intestine worm counts (L) numbers of eosinophils, ILC2s and Th cells (M) in lungs were assessed in irradiated chimeric Rag2−/− gc−/− mice reconstituted with the bone marrow from either wild-type (n=5) or Ramp1 −/− (n=5) mice infected with N. brasiliensis on day 9 post infection. Each symbol represents an individual mouse (C-F, H-I, K-M). Statistical significance is depicted as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 (Student’s t-test). Data are from representative (B, H, I) or pool (C-F) of two experiments with similar results or from one experiment (K-M). See also Figure S6.