Figure 3. THZ1 downregulates c-MYC, MCL-1 and BCL-XL transcriptional and overexpression of c-MYC, MCL-1, or BCL-XL significantly diminishes apoptosis induced by THZ1.
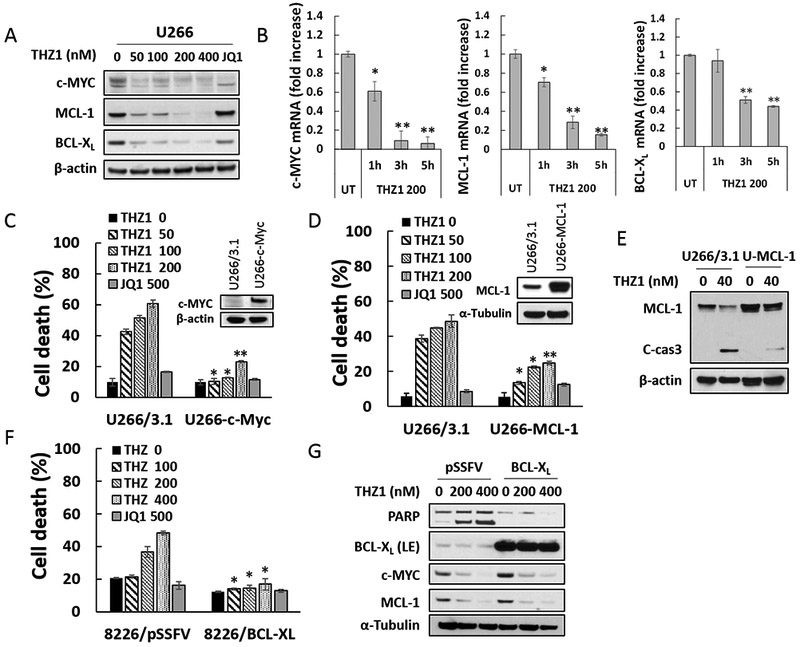
(A) U266 cells were treated with THZ1 or the BET inhibitor JQ1 (500 nM) for 24 hr, after which c-MYC, MCL-1 and BCL-XL proteins were monitored by immunoblotting analysis. β-actin was assayed to ensure equivalent loading and transfer. (B) U266 cells were exposed for 1, 3, or 5 hours to THZ1 (200 nM), after which RNA was extracted from the cells. Expression of c-MYC, MCL-1 and BCL-XL were analyzed by real-time RT-PCR, and results are presented relative to GAPDH expression in the un-treated control group. (C and D) U266 cells were stably transfected with pcDNA3.1, pcDNA3.1-c-MYC, or pcDNA3.1-MCL-1. Cells were treated with THZ1 or the BET inhibitor JQ1 (500 nM) for 24 hr, after which cell death was analyzed by flow cytometry following staining with 7-AAD. Values represent the means ± SD for at least three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *P<0.05; **P<0.01 (E) Transfected U266 cells were treated with the indicated concentration of THZ1 for 24 hr. MCL-1 and caspase-3 cleavage were monitored by immunoblotting analysis. β-actin was assayed to ensure equivalent loading and transfer. (F and G) 8226 cells stably transfected with pSSFV (empty vector) or BCL-XL, were treated with THZ1 or the BET inhibitor JQ1 (500 nM) for 24 hr. Cell death was analyzed by flow cytometry following staining with 7-AAD. Expression of PARP, BCL-XL, c-MYC, and MCL-1 were monitored by immunoblotting analysis. α-Tubulin was assayed to ensure equivalent loading and transfer.
