Figure 6. THZ1 reduces tumor burden and significantly enhances survival in flank and orthotopic xenograft mouse MM models with minimal toxicity.
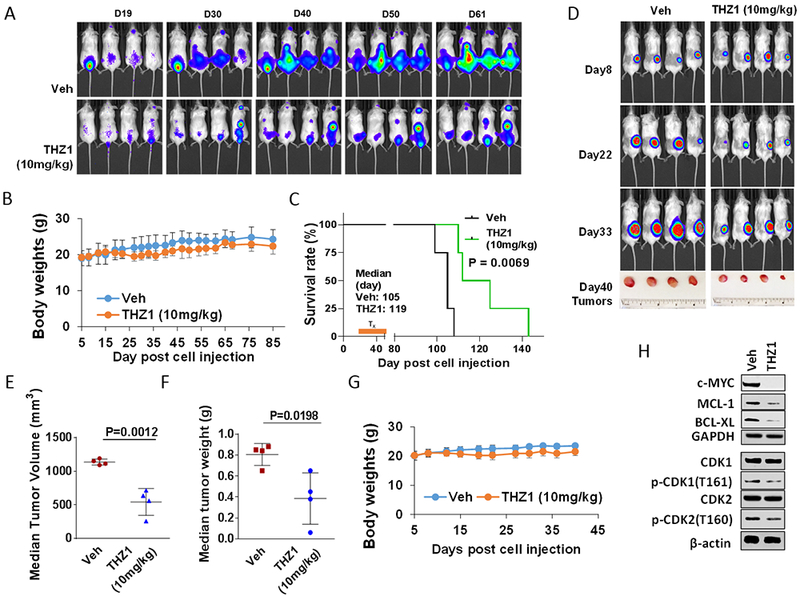
(A-C) NOD/SCID-γ (NSG) mice were injected intravenously via tail vein with 5×106 U266 cells stably expressing luciferase. After signals were visible (10 days after injection of tumor cells), THZ1 (10 mg/kg, i.p.) was administered daily for 5 days/week for an additional 4 weeks; n = 4 per group. Control animals were treated with equal volumes of vehicle. (A) Tumors were monitored every other day after i.p. injection with 150 mg/kg luciferin using the IVIS 200 imaging system. Veh, vehicle. (B) Survival of the animals was determined by Kaplan–Meier analysis. Inset, median survival days. P-values indicate significant difference between groups. (D-H) NSG mice were subcutaneously (s.c.) inoculated in the right rear flank with 5×106 luciferase-expressing U266 cells. Treatment was initiated after a luciferase signal was detected. THZ1 (10 mg/kg, i.p.) was administered daily for 5 days a week for an additional 4 weeks; n = 4 per group. Control animals were administered equal volumes of vehicle. (D) Tumors were monitored every other day after i.p. injection with 150 mg/kg luciferin using the IVIS 200 imaging system. Veh, vehicle. (E and F) Tumors were removed and weighed at day 40 after cell injection. Tumor volume was then plotted against actual tumor weight for each individual mouse. (C and G) Mice did not display significant body weight loss (>20% of initial weight) or other signs of toxicity due to the treatment. (H) Western blot analysis was performed to monitor the indicated candidate pharmacodynamic markers, identified from in vitro experiments, in tumors excised from representative mice.
