Figure 1.
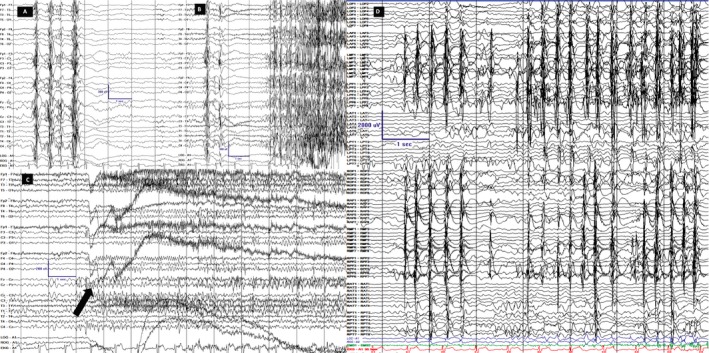
Scalp and invasive EEG recordings. LFF 1Hz; HFF 70Hz, Notch OFF; Sensitivity 7 uV/mm Timebase 30mm/sec. Scale is displayed in all images; y‐axis is amplitude in uV and x‐axis is time in seconds. Scalp (A–C) and intracranial (D) recordings are on longitudinal bipolar montage along with coronal ring on scalp. A. Interictal background displayed generalized PSSW (polyspike, spike and slow wave) discharges without hemispheric predominance B. Tonic seizure. The first unequivocal ictal electrographic change occurred as burst of generalized PSSW followed by electro‐decrement and generalized FFA (faster frequency activity). The first ictal behavior occurred 2‐3 seconds after the first EEG change. C. Hypermotoric seizure. The first unequivocal electrographic change occurred as generalized, centrally predominant, medium amplitude FFA (arrow) and clinically evidenced by eyelid myoclonia followed by myoclonus of legs and flailing of left hand. D. Typical brief hypermotoric and myoclonic seizure evidenced at onset by synchronous periodic discharges from the RPF (right posterior frontal)/ RMF (right middle frontal)/ RAF (right anterior frontal)/ ROF (right orbitofrontal)/ LMF (left middle frontal)/ LAF (left anterior frontal)/ LPF (left posterior frontal) highest in amplitude on the lateral contacts.
