Figure 1.
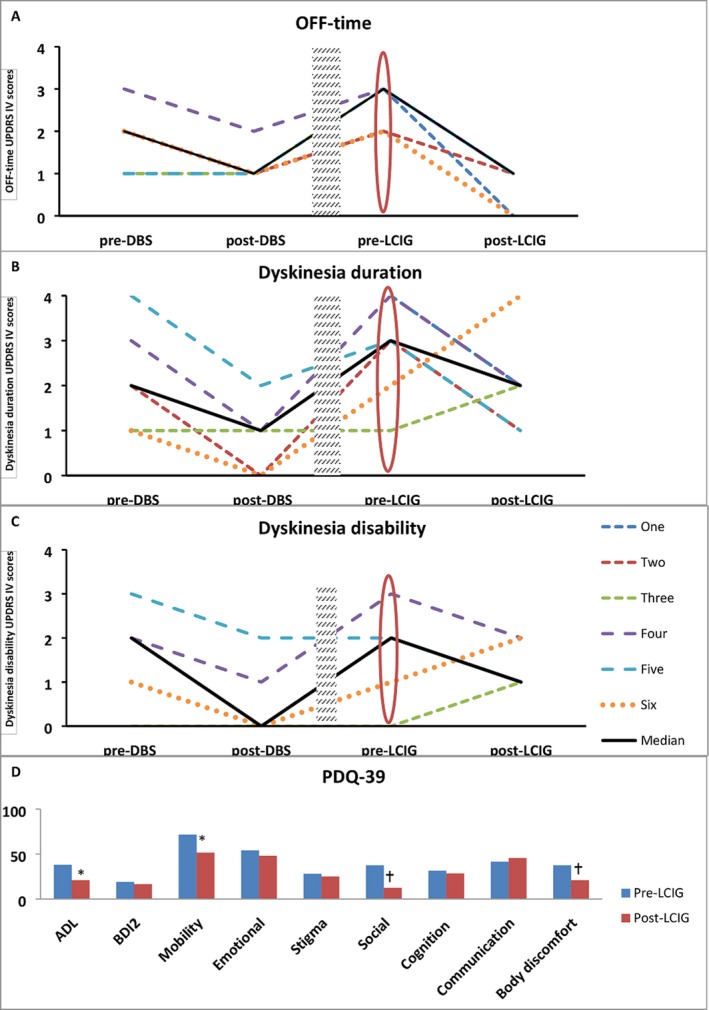
(A and B) show respectively off‐time and dyskinesia duration scales; 0: No dyskinesia, 1: 25% or less, 2: 25–50%, 3: 51–75%, 4: 76–100% of daytime hours. (A) Off‐time duration decreased in three patients after DBS surgery and uniformly decreased after LCIG therapy in all patients regardless of DBS target, laterality or accuracy of lead location (patient one had no UPDRS IV pre‐ and post‐DBS). (B) Dyskinesia duration decreased in five patients after DBS therapy but only in four patients after receiving LCIG therapy. (C) Dyskinesia disability scale 0: Not disabling, 1: mildly disabling, 2: moderately disabling, 3: severely disabling, 4: completely disabled. Dyskinesia disability decreased in four patients after DBS surgery and in three patients after LCIG therapy (patient one had no UPDRS IV pre‐ and post‐DBS). Shaded rectangle is disease progression (range 1–8 years). Red oval is the new baseline after disease progression but prior to implementation of LCIG therapy. (D) Median Quality of life scores pre‐ and post‐LCIG therapy in four patients. ADL (activity of daily living), BDI2 (Beck Depression Inventory 2). Trend toward significance (*P = 0.068) was seen in ADL and Mobility scores and in social and body discomfort scores († P = 0.109) using Wilcoxon Signed Rank test to compare medians.
