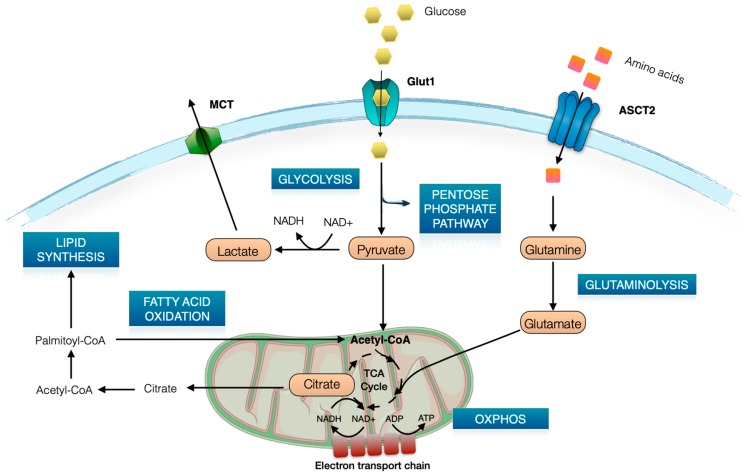
Figure 1.
Schematic summary of the metabolic network. ATP can be generated from glucose though two integrated pathways. Glucose enters the cell via Glut1 and undergoes to enzymatic breakdown to pyruvate in the glycolysis pathway in the cytoplasm. The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle encompasses the second pathway, where pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA in the mitochondria to fuel oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Anaerobic glucose catabolism transforms pyruvate into lactate that is transported out of the cell. Other substrates can also be metabolized in the TCA cycle, such as fatty acids via β-oxidation and glutamine via glutaminolysis.