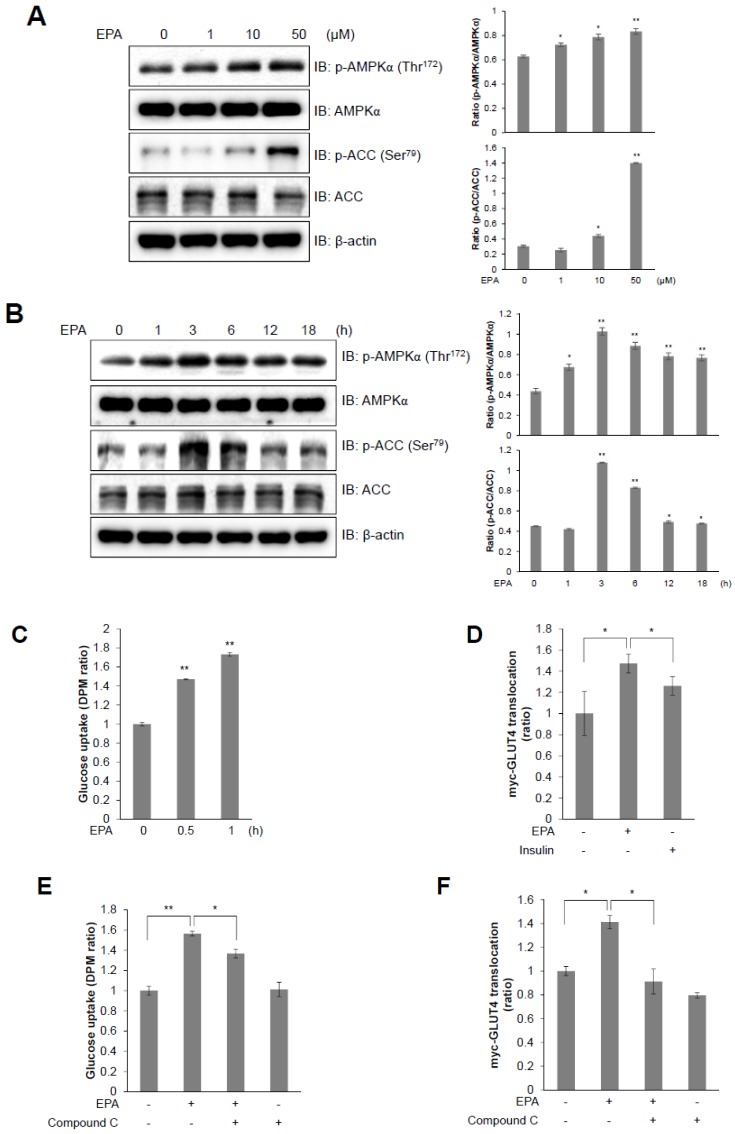
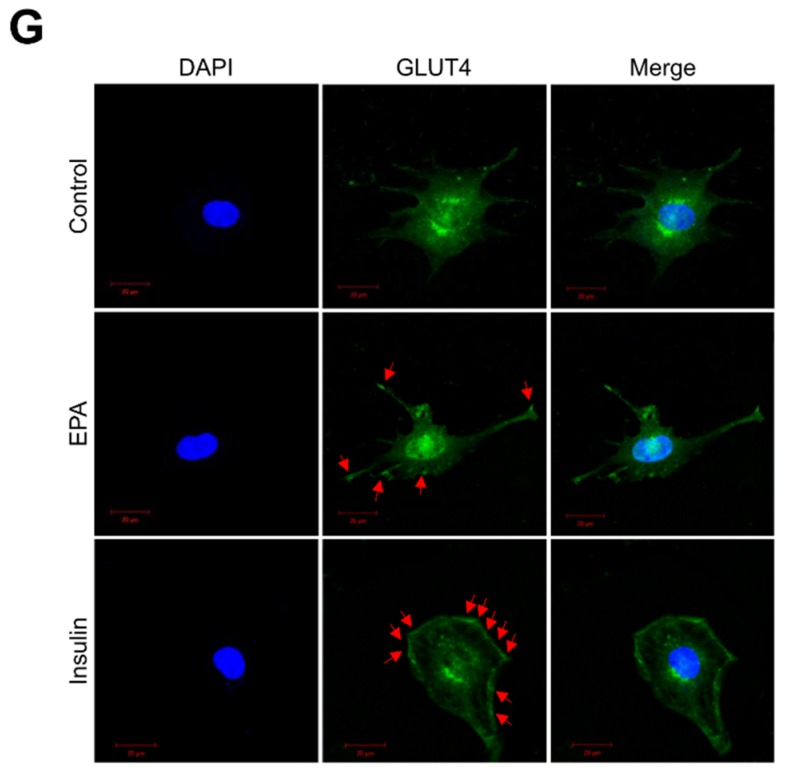
Figure 2.
T EPA stimulates glucose uptake through the AMPK signaling pathway in C2C12 myoblasts. (A) Western blot analysis of AMPKα and ACC phosphorylation in C2C12 cells treated with various concentrations of EPA for 3 h or (B) 30 µM EPA for the indicated times. Total protein levels for AMPKα, ACC and β-actin were used as loading controls. (C) 2-deoxy-d[H3]-glucose (2-DG) uptake measured in L6 cells differentiated for 7 days and treated with 50 μM EPA for the indicated times. (D) Cell surface expression of Myc-GLUT4 quantified using an antibody-coupled colorimetric absorbance assay in myoblasts stably expressing L6-GLUT4-myc, differentiated for 7 days, and treated with EPA or 100 nM insulin for 3 h. (E) Differentiated L6 myotubes treated with 50 μM EPA for 3 h in either the presence or absence of compound C (5 μM). (F) Differentiated L6-myc-GLUT4 cells were pre-treated with compound C for 30 min, and then incubated with EPA for 3 h. The Myc-GLUT4 expression in cells is quantified using an absorbance assay. (G) Representative images (GLUT4, DAPI, and merge) of cells treated with EPA for 3 h. Insulin (100 nM) was used as positive control. Scale bar, 20 μm. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 compared to untreated cells. Results from three independently replicated experiments are presented.