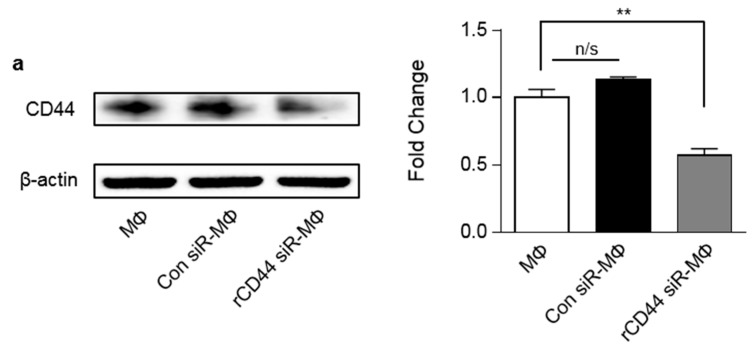
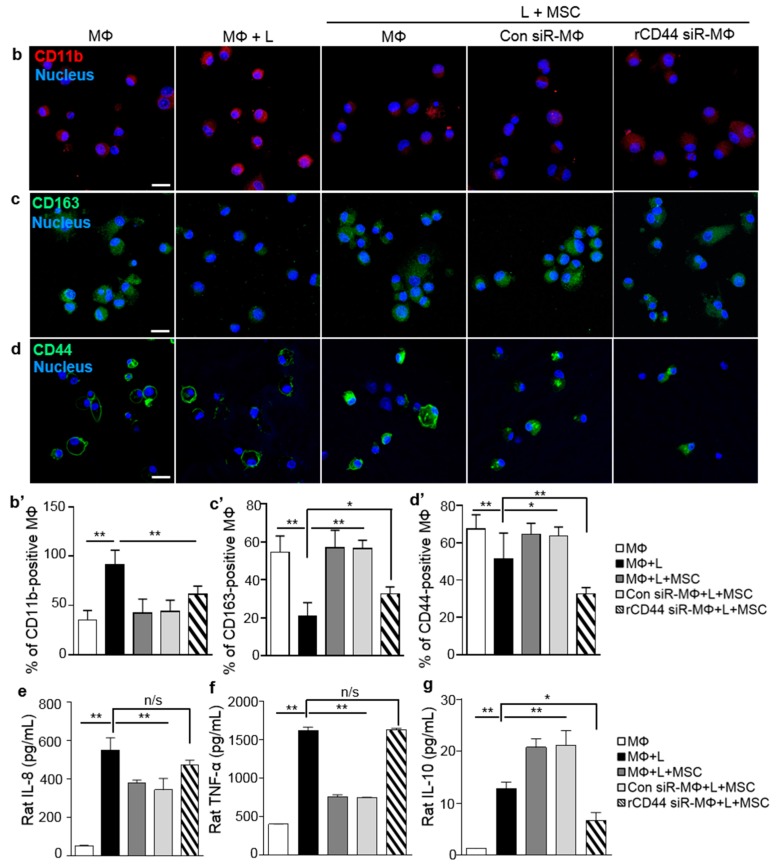
Figure 2.
Modulation of macrophage functional polarity towards an anti-inflammatory phenotype by MSCs occurs via CD44 on rat macrophages. (a) Rat macrophages were transfected with scrambled siRNA (50 nM) or rat CD44 siRNA (50 nM) for 24 h. After CD44 siRNA transfections, LPS stimulation was performed. Rat CD44 protein expression on macrophages was analyzed by western blotting. Intensity was normalized to macrophages only. (b,b’–d,d’) CD44 knockdown in macrophages disrupted macrophage polarization. Confocal microscopy of CD44 siRNA-transfected macrophages showed an increased expression of the M1 marker, CD11b and decreased expression of the M2 marker, CD163, despite treatment with MSCs. Quantitative analysis showed the significant results of knockdown CD44 on macrophages. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342. Red (CD11b) and green (CD163 and CD44) staining indicate positive cells. (e–g) Cytokine analysis was performed by ELISA. Supernatants from CD44 siRNA-transfected macrophage cultures also showed high levels of IL-8 and TNF-α, but low levels of IL-10. Scale bar = 20 μm. Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 5 per group. ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05. n/s, not significant; MΦ, macrophage; L, LPS; Con siR, scrambled siRNA-transfected control group; rCD44 siR, rat CD44 siRNA-transfected group.