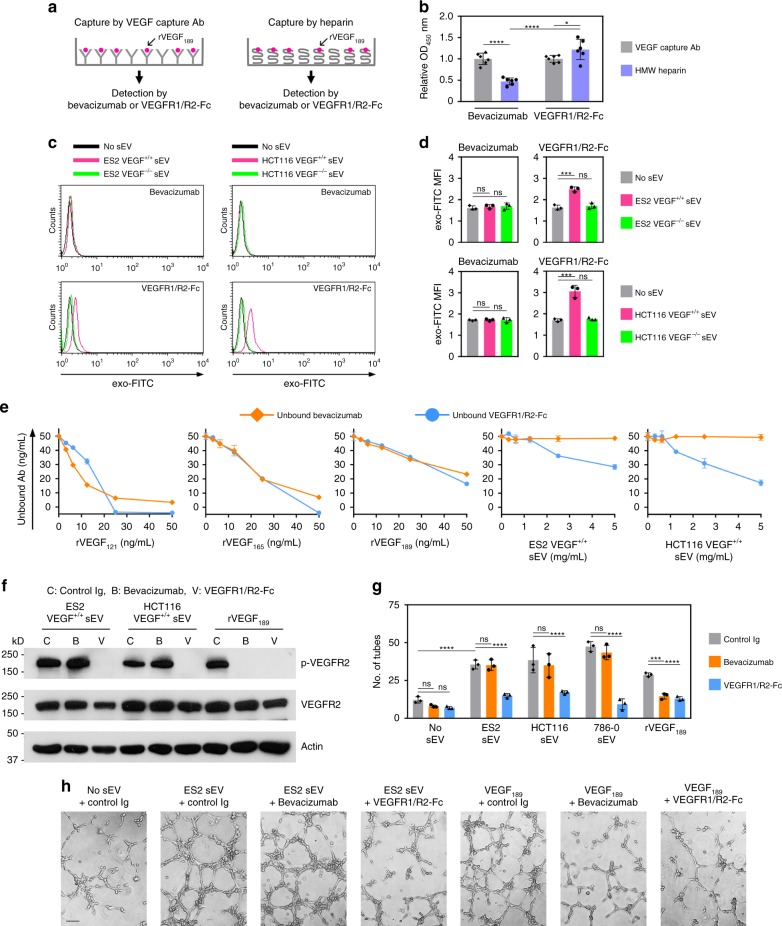
Fig. 7.
Heparin-bound sEV-VEGF is not neutralized by bevacizumab in vitro. a, b rVEGF189 was captured by HMW heparin or by VEGF capture Ab (positive control), and then incubated with bevacizumab or VEGFR1/R2-Fc. Bevacizumab bound to VEGF189 and VEGFR1/R2-Fc bound to VEGF189 were detected by anti-human IgG. In a, experimental scheme. In b, relative levels of bevacizumab bound to VEGF189 and VEGFR1/R2 bound to VEGF189. Shown are mean ± SD of n = 6 independent experiments. c, d Microbeads were coupled to bevacizumab, incubated with sEVs of VEGF+/+ cells or sEVs of VEGF−/− cells, and then stained with exo-FITC dye to label sEV membrane. The same procedure was performed using microbeads coupled to VEGFR1/R2-Fc (positive control). Binding of bevacizumab and VEGFR1/R2-Fc to VEGF on the surface of sEVs was evaluated by flow cytometric analysis of exo-FITC fluorescence in the gated population of microbeads. In c, representative histogram plots. In d, MFI values of n = 3 independent experiments (mean ± SD). Gating strategy is shown in Supplementary Fig. 6a. Contour plots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 14a. e Bevacizumab and VEGFR1/R2-Fc were incubated with recombinant VEGF and with sEVs that have a VEGF content equivalent to the range of amounts of recombinant VEGF. Following incubation, levels of unbound bevacizumab and unbound VEGFR1/R2-Fc were assayed. Shown are mean ± SD of n = 3 independent experiments. f–h HUVEC were stimulated with sEVs or rVEGF189 that were pre-incubated with control Ig, bevacizumab, or VEGFR1/R2-Fc, and then assayed for phosphorylated and total VEGFR2 (f) and tube formation (g, h). In g, mean ± SD of n = 3 independent experiments. In h, representative images of tube formation. Scale bar = 100 μm. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 by ANOVA with Bonferroni’s corrections; one-way in d; two-way in b and g. Source data used for graphs in b, d, e, and g can be found in Supplementary Data 6