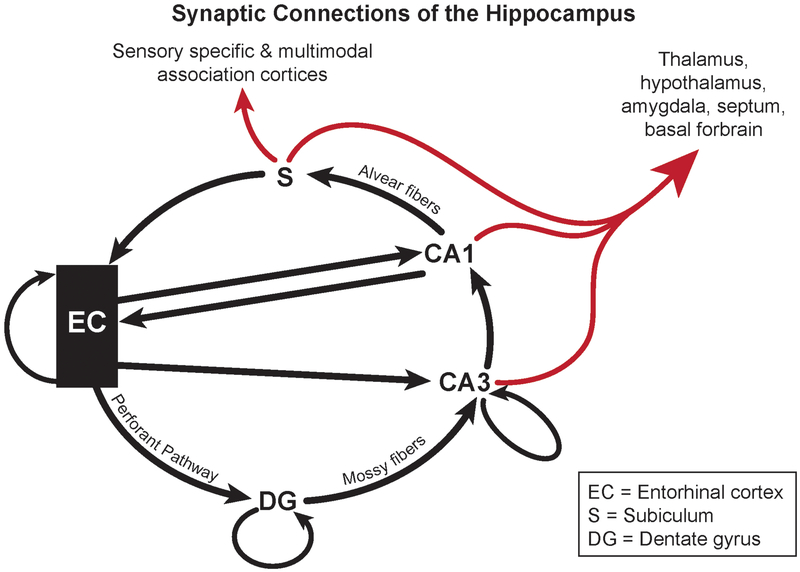
Fig. 3.
The synaptic connections of the hippocampus. The entorhinal cortex (EC) layer II neurons input to hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons via the dentate gyrus (DG) mossy fiber synapses of the granule cells in a laminar fashion. CA3 pyramidal neurons input to the pyramidal neurons in CA1, thus forming the trisynaptic loop (EC to DG to CA3 to CA1). CA1 neurons project to the subiculum via the Alvear fibers. The EC also directly inputs to the CA1 and CA3. The EC, DG and CA3 also project back within themselves. Black arrows indicate entorhinal-hippocampal pathways, red arrows indicate pathways leading to other parts of the brain. Adapted from Amaral and Witter’s scheme [2]