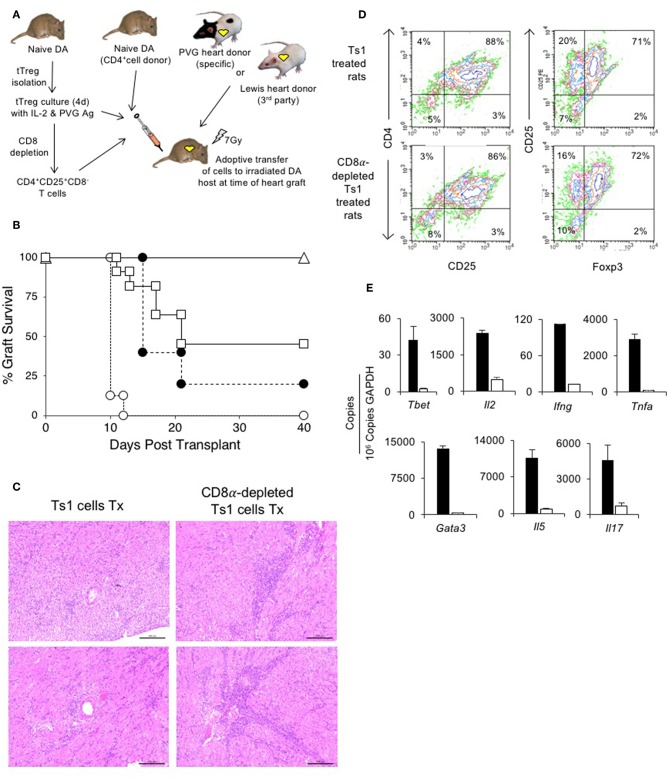
Figure 5.
Assessment of suppression by CD8α expressing CD4+CD25+T cells in an adoptive model of cardiac allograft rejection. (A) Scheme of experimental protocol. Irradiated DA hosts were transplanted with PVG heart allograft and given 5 × 106 CD4+T cells prepared from naïve DA rats. In this model, irradiated rats do not reject their graft unless reconstituted with naïve CD4+T cells that restore rejection in 10–14 days (25). 5 × 106, but not 5 × 105, freshly isolated CD4+CD8α−CD25+ tTreg suppress rejection in hosts restored with 5 × 106 naïve CD4+T cells (25). In previous studies, we showed 0.5 × 106 unfractionated Ts1 cells could suppress rejection of specific donor but not third-party Lewis heart grafts (33). To examine role of CD8α+Treg in unfractionated Ts1 cell populations, the unfractionated Ts1 cells were produced after culture of naïve tTreg with PVG stimulator cells and rIL-2 for 4 days. CD8α+ cells were depleted and the capacity of 5 × 105 CD8α-depleted Ts1 cells to suppress rejection was examined and was compared to that of unfractionated Ts1 cells. (B) Survival of PVG cardiac allografts in irradiated DA rats restored with 5 × 106 naïve CD4+T cells: effect of CD8α depletion on ability of Ts1 cells to suppress allograft rejection and induce tolerance. 0.5 × 106 unfractionated Ts1 cells suppressed rejection in all hosts with grafts surviving >100 days (Δ) (n = 9). This was significantly different to rats that received no Treg and were given 5 × 106 naïve CD4+T cells only (O) that rejected their grafts in less than 2 weeks (n = 8) (p < 0.001). To test the effect of CD8α+ cells, Ts1 cells were depleted of CD8α+ cells by panning as described in Methods. 0.5 × 106 CD8α-depleted Ts1 cells (□) given with 5 × 106 naïve CD4+ T cells (n = 11), did not prevent rejection and over halve the animals had rejected their graft within 22 days. This was significantly different to hosts given the same number of unfractionated Ts1 cells that contained CD8α+cells (p < 0.05), as well as to control rats given no Treg which had more rapid rejection (p < 0.001). 0.5 × 106 fresh tTreg (∙) (n = 5) delayed rejection compared to controls given no Treg (p = 0.05) and their effect was similar to the CD8α-depleted Ts1 cells. These results showed that CD8α+ cells in the unfractionated Ts1 cells were required to mediate full suppression of allograft rejection. CD8α+-enriched (CD4+CD8α+CD25+T) cells could not be trialed as the anti-CD8 mAb (MRC Ox8) used to enrich these cells opsonizes these cells in vivo (44). Results are combined data from four separate experiments. (C) Histology of allografts in hosts given unfractionated Ts1 cells or CD8α-depleted Ts1 cells. Photomicrographs of H&E stained cardiac allografts from adoptive hosts 40 days after they were given naïve CD4+T cells and either unfractionated Ts1 or CD8α-depleted Ts1 cells. Images taken using a Leica DFC 450C camera on a Leica DM 2000 LED microscope using a 20x magnification. Heart grafts from hosts given CD8α-depleted Ts1 cells had large areas of mononuclear cell infiltration and scattered infiltrate between myocytes. There were wide areas of myocyte necrosis. Heart grafts from animals given unfractionated Ts1 cells had minimal mononuclear infiltration between myocytes and minimal myocyte necrosis. (D) FACS profiles of CD25+T cells enriched from spleen and lymph nodes of adoptive hosts restored with unfractionated Ts1 cells or CD8α-depleted Ts1 cells. Spleen and LN from adoptive hosts given naïve CD4+T cells and either unfractionated Ts1 or CD8α-depleted Ts1 cells were harvested and single cell suspension prepared. Lymphocytes were subjected to single step isolation of CD25+T cells. There was no difference in the proportion of CD25+ or Foxp3+ populations. These cells were used to prepare mRNA for RT-PCR shown in (E). (E) RT-PCR of CD25+T cells prepared from adoptive hosts restored with naïve CD4+T cells and either unfractionated Ts1 cells or CD8α-depleted Ts1 cells. The CD25+enriched populations from rats restored with unfractionated Ts1 populations (white bars) and from CD8α-depleted populations (black bars) were subjected to RT-PCR to determine expression of cytokine receptors, transcription factors and cytokines. Cells from hosts that were given CD8α-depleted Ts1 had higher expression of Th1 and Th2 transcription factors, Tbet and Gata3 and cytokine such as Il2, Ifng, Tnfa, Il17, and Il5 consistent with increased inflammation and graft rejection. These findings suggest the CD8α-depleted Ts1 cells were not able to control rejection response and the CD25+ cells isolated from these hosts had activated effector cells that expressed mRNA for Th1 and Th2 cytokines.