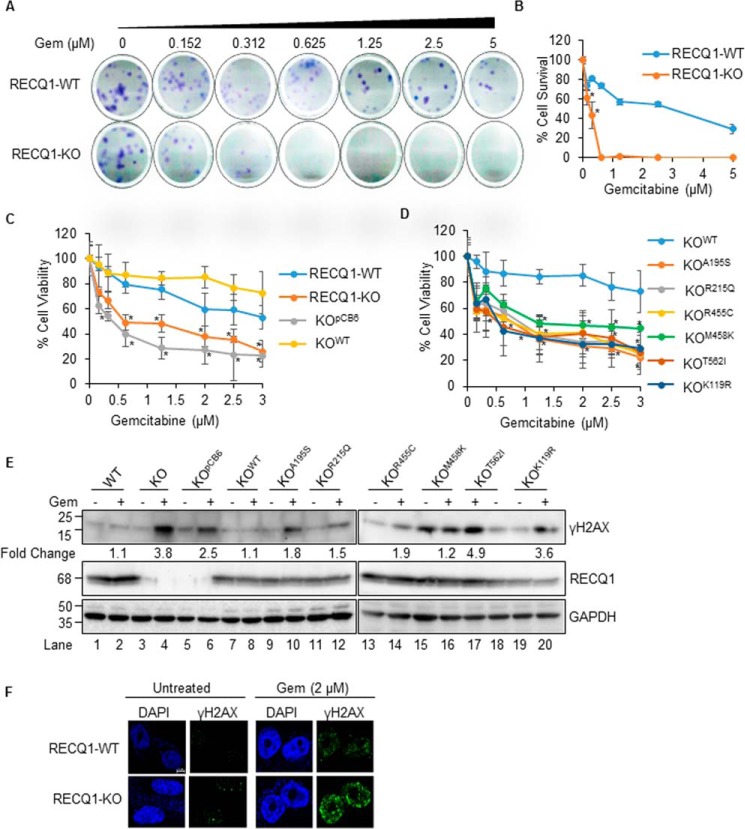
Figure 2.
Catalytic functions of RECQ1 are important in resolving DNA damage induced by nucleoside analog gemcitabine in MDA-MB-231 cells. A, representative images of colony formation assay of RECQ1-WT and RECQ1-KO cells treated with gemcitabine (Gem). B, quantification of clonogenic survival assay after gemcitabine treatment in RECQ1-WT and RECQ1-KO cells. The graph represents the means (± S.D.) from three independent experiments, and the statistical significance (p < 0.05) between the two cell types is indicated by an asterisk. C and D, drug sensitivity to gemcitabine in RECQ1-WT, RECQ1-KO, and complemented lines. Cell viability data are presented as means (± S.D.) from three independent experiments. The statistical significance of cell viability changes among RECQ1-WT versus other groups is indicated as an asterisk (p < 0.05). Differences are not statistically significant unless denoted by an asterisk. E, Western blotting analysis of γH2AX in the indicated cells treated with gemcitabine (0.1 μm for 24 h). GAPDH is used as a loading control. The load order for untreated and gemcitabine-treated samples from KOT562I cells is reversed. Fold change in gemcitabine-induced γH2AX compared with the respective untreated condition was determined by quantification of signal intensities using ImageJ. F, representative immunostaining images of γH2AX in RECQ1-WT and RECQ1-KO cells untreated or treated with gemcitabine (2 μm for 2 h). DAPI is used as a nuclear stain. The scale bar is 5 μm and represents all images in Fig. 2F. Molecular mass (in kDa) is shown to the left of the Western blots.