Figure 1.
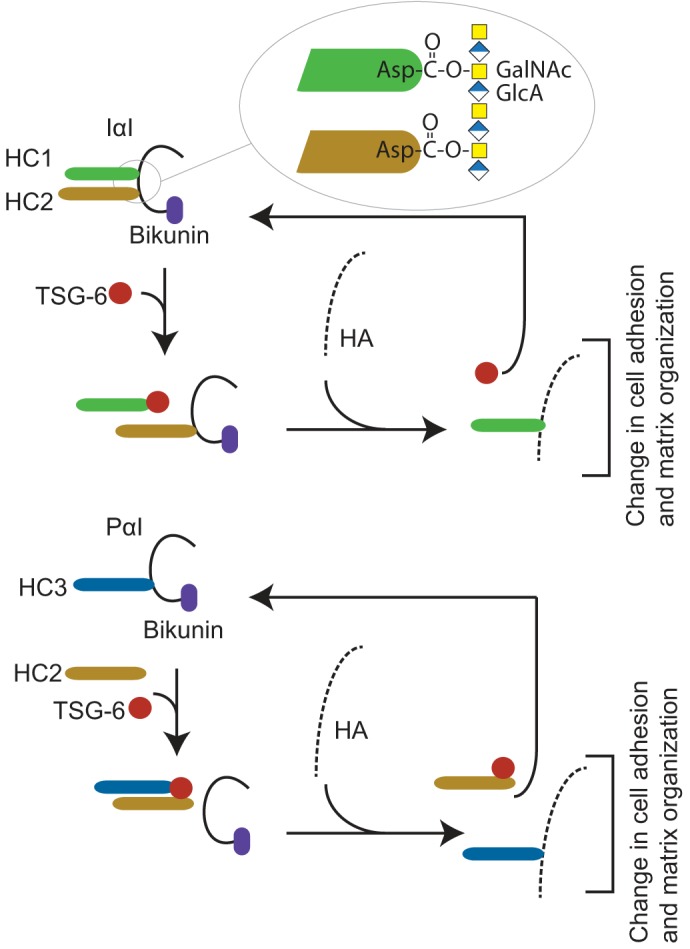
Overview of the human IαI- and TSG-6–mediated HC transfer. IαI is composed of bikunin and two homologous heavy chains (HC1 and HC2) (top). The HCs are covalently linked to the CS chain by a unique ester bond between the C terminus and N-acetylgalactosamines in the CS chain (inset) referred to as a PGP cross-link (2, 3, 5). In the ECM, IαI stabilizes HA-rich matrixes in a process requiring TSG-6 expressed during inflammatory disease states (13–15). TSG-6 catalyzes the transfer of HCs from IαI to HA, generating covalent HC–HA complexes (16). PαI is composed of bikunin linked to HC3 (bottom) (1, 2). The presence of HC2 is essential for the TSG-6–mediated transfer of HC3 to HA (12). The HC transfer reaction takes place in the presence of divalent cations and when the TSG-6 and bikunin proteins colocalize, e.g. during inflammation (17). The transfer of HC to HA changes the characteristics of the HA matrix and affects cell adhesive properties and matrix organization (18–20).
