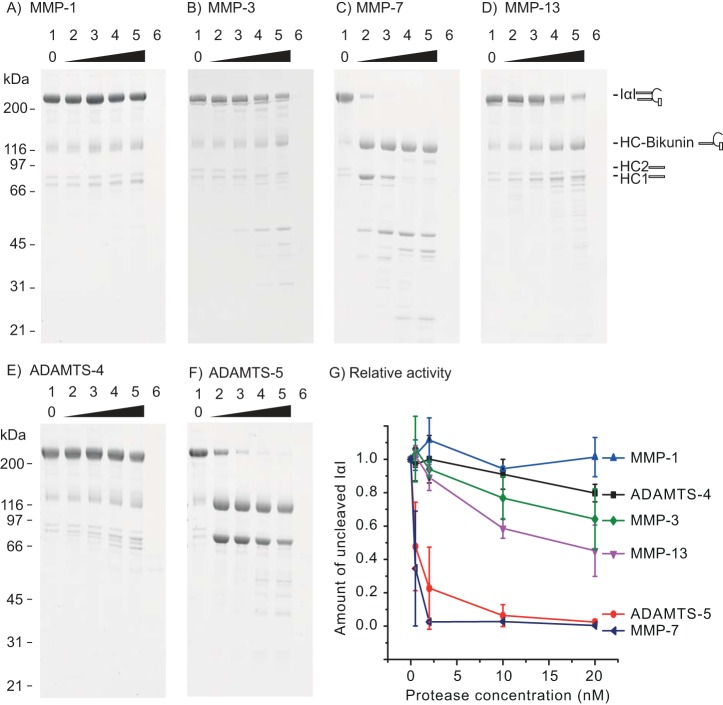
Figure 2.
IαI is a substrate for MMP-3, MMP-7, MMP-13, and ADAMTS-5. A fixed amount of IαI was incubated with increasing amounts of the indicated proteases for 16 h at 37 °C before being analyzed by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Blue (A–F). The concentration of IαI was 0.9 μm, and the concentration of the protease was 0, 0.5, 2, 10, and 20 nm (lanes 1–5). The protease alone at 20 nm was loaded as a control (lane 6). Molecular mass size markers are indicated on the left side (kDa). The schematics on the right side of the gels show the migration of intact IαI, HC–bikunin, HC2, and HC1 alone. In lane 1, IαI appears together with HC–bikunin and free HCs as a result of nonenzymatic autohydrolysis of the ester in the PGP cross-link. The relative rate of IαI proteolysis by the tested proteases was evaluated by densitometry (G). The amount of noncleaved IαI at different protease concentrations was normalized to the IαI control (lane 1). The error bars represent the standard deviation of at least three experiments. In conclusion, these data show that MMP-3, MMP-7, MMP-13, and ADAMTS-5 are able to cleave IαI, which is demonstrated by the progressive reduction of the IαI level, accompanied by the occurrence of proteolytic degradation products.