Figure 5.
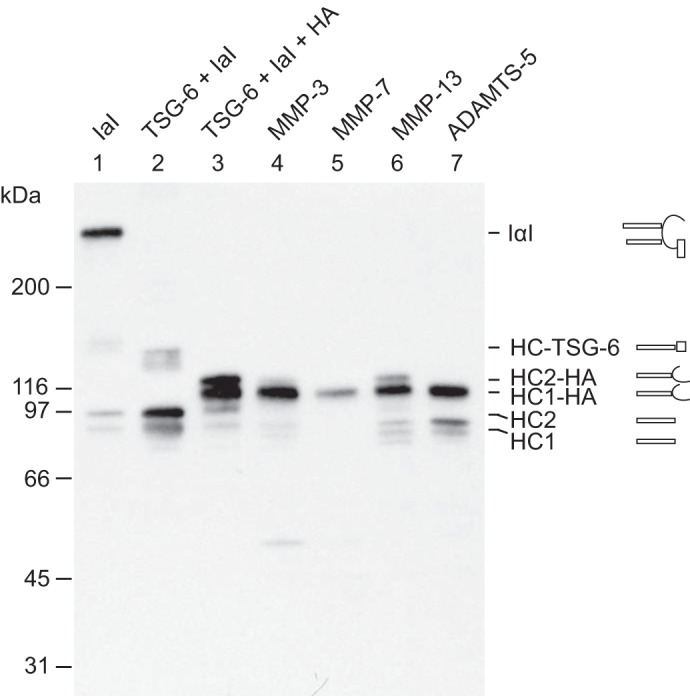
ADAMTS-5, MMP-3, MMP-7, and MMP-13 are able to cleave HC2 when covalently linked to HA. IαI (lane 1) was incubated with TSG-6 alone (lane 2) or with both TSG-6 and HA oligomers (lane 3). After 4 h at 37 °C, the protease was added to the HA-containing sample (lanes 4–7), which was then incubated for 16 h in parallel with the control sample (lane 3). All samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using an anti-HC antibody. Schematics of the subunit compositions of the bands are shown on the right side of the gel. As expected, the migration of the HCs transferred to HA by HC2/TSG-6 (lane 3) was slower than that of the free HCs. The migration of the free HCs is shown in lane 1 as a result of nonenzymatic autohydrolysis of the ester in the PGP cross-link. Following proteolysis (lanes 4–7), the bands corresponding to HC2–HA are reduced or absent. The degradation products can be observed following MMP-13 or ADAMTS-5 treatment (lanes 6 and 7). MMP-3 and -7 (lanes 4 and 5) apparently cleave HC2 into fragments that are not recognized by the antibody. The data represent four experimental repeats. These data show that HC2 cross-linked to HA still acts as a substrate for MMP-3, MMP-7, MMP-13, and ADAMTS-5.
