Figure 7.
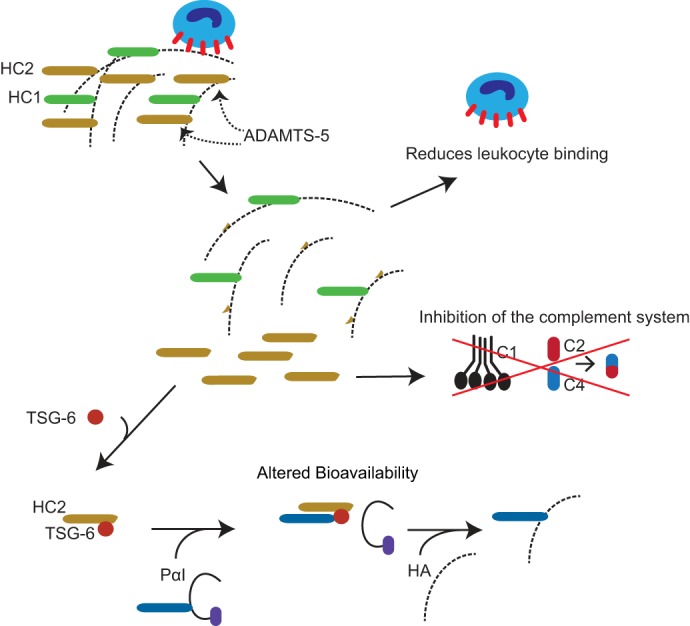
Potential consequences of ADAMTS-5–mediated HC2 release from HA. ADAMTS-5–mediated release of HC2 may change the stability and cell-binding properties of HA. In addition, it has previously been shown that the transfer of HCs to HA increases the binding of HA to its primary cell surface receptor, CD44, on leukocytes (20). Consequently, the release of HC2 may inhibit leukocyte adhesion to the HA-rich matrix. HC2 also affects complement activation (42), and the ADAMTS-5–mediated release of HC2 may therefore provide a mechanism for local regulation of the immune response. Furthermore, the bioavailability and mobility of the HC2–TSG-6 complex will be affected when HC2 is released from HA in the ECM.
