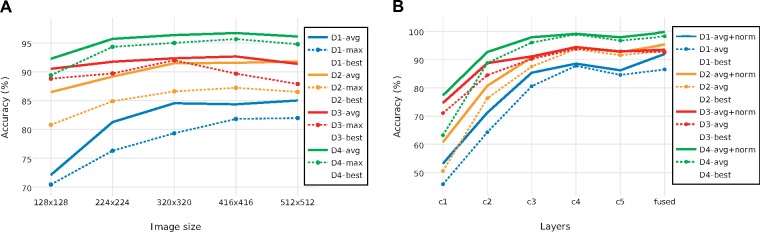
Figure 4.
a) Impact of image size and average versus max global pooling of c5 features on identification accuracy. Data sets are separated by color, and the best result for each data set is indicated with a cross (X). Global average pooling was always better than global max pooling. In general, 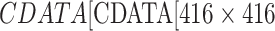 tended to be the best image size. It was the optimal size for two out of four data sets (global average pooling) or three out of four data sets (global max pooling). b) Impact of feature depth, normalization and feature fusion on identification accuracy. Input images of size
tended to be the best image size. It was the optimal size for two out of four data sets (global average pooling) or three out of four data sets (global max pooling). b) Impact of feature depth, normalization and feature fusion on identification accuracy. Input images of size 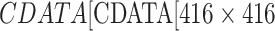 and average global pooling was used in all cases. Data set colors and indication of the settings giving the best identification performance as in (a); note that the performance of feature fusion here is slightly different from that in (a) because of minor differences in the protocol between the experiments. Normalization and feature fusion generally improved identification accuracy, although c4 features tended to outperform features from all other individual layers.
and average global pooling was used in all cases. Data set colors and indication of the settings giving the best identification performance as in (a); note that the performance of feature fusion here is slightly different from that in (a) because of minor differences in the protocol between the experiments. Normalization and feature fusion generally improved identification accuracy, although c4 features tended to outperform features from all other individual layers.