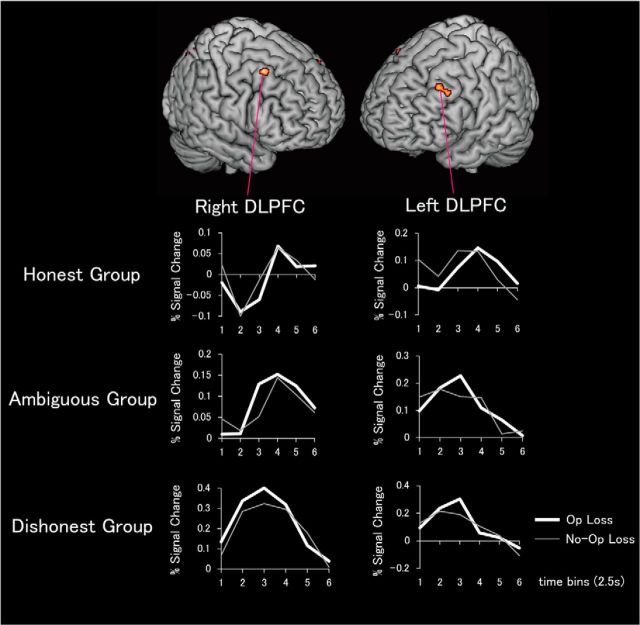
Figure 3.
Response to anticipated reward in the nucleus accumbens predicts DLPFC activity when refraining from gaining money dishonestly (n = 26). Bilateral DLPFC regions exhibited positive correlations (p < 0.001, uncorrected) between mean response to anticipated reward in the nucleus accumbens (averaged across right and left regions) during the MID task and the difference in mean signal change for chosen (Opportunity) Loss trials versus forced (No-Opportunity) Loss trials. Graphs show time courses of mean decision-related percentage change in BOLD signal during the coin-flip task for the honest, ambiguous, and dishonest groups. Signal time courses are displayed across 6 time-bins of 2.5 s each.