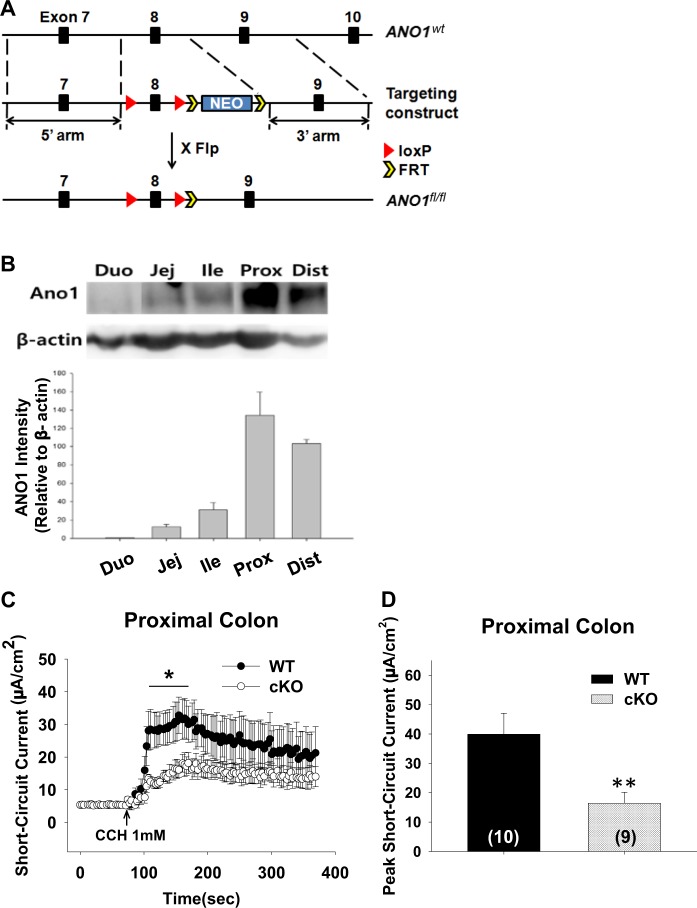
Fig. 1. Ablation of Ano1 from intestinal epithelial cells reduces carbachol-induced transepithelial Cl− currents.
a Schematic diagram for the construction of the Ano1fl/fl mice. Exon 8 of Ano1 was flanked by loxp sites. The Ano1fl/fl mice were crossed with Cdx2-cre transgenic mice to obtain Cdx2-Ano1fl/fl mice. b Western blots of ANO1 in intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) isolated from intestinal segments in mice. IECs were prepared from each segment of the small and large intestines. Actin is a loading control. The whole blot is shown in Supplementary Fig. 3. The experiments were repeated four times. duo; duodenum, jej; jejunum, ile; ileum, prox; proximal colon, dist; distal colon. c Changes in short-circuit currents evoked by 1 mM carbachol applied to the serosal surface of the colon isolated from Ano1fl/fl (wild-type, WT) and Cdx2-Ano1fl/fl (conditional knockout, CKO) mice. To block Na+ and K+ currents, 100 μM amiloride and 5 mM BaCl2 were added to the mucosal and serosal sides, respectively. d Summary of peak short-circuit currents evoked by carbachol applied to the colon of WT and Cdx2-Ano1fl/fl (CKO) mice. **p < 0.01 and *p < 0.05. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). The numbers in brackets represent the number of experiments