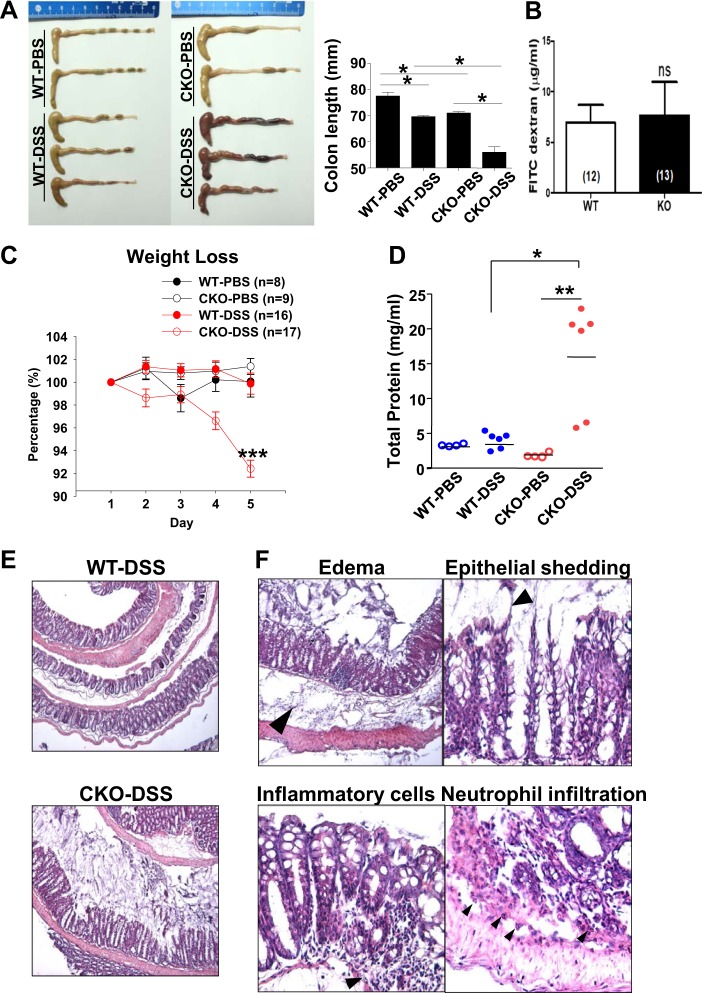
Fig. 6. Acute treatment with dextran sodium sulfate induces severe colitis in CKO mice.
a Colons isolated from Ano1fl/fl (WT) and Cdx2-Ano1fl/fl (CKO) mice were treated orally with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) or 2% DSS-containing saline solution for 5 days. A greater reduction in the length of the colons from the CKO mice was observed after treatment with DSS. (Right) Summary of the colon lengths from both genotypes after treatment with PBS or DSS. *p < 0.05. b The barrier functions of the guts of WT and Cdx2-Ano1fl/fl (KO) mice. The barrier function was determined by the dextran permeability through the gut. ns, not significant. c Changes in body weights of WT and CKO mice treated with PBS or DSS from day 1 to day 5. ***p < 0.001 compared to WT mice treated with DSS. d Total amount of protein extracted from feces collected from both genotypes on the fifth day after treatment with PBS or DSS. Horizontal bars represent the means. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. e Hematoxylin and eosin-stained colonic sections of Ano1fl/fl (WT) and Cdx2-Ano1fl/fl (CKO) mice treated with DSS. f Magnified sections of colons from CKO mice stained with hematoxylin and eosin. The submucosal layer was edematous (arrowhead), the epithelium was irregular (arrowhead) because of shedding, mononuclear cells (arrowhead) were prominent, and neutrophils (arrowhead) had infiltrated the submucosal layer in colons from CKO mice