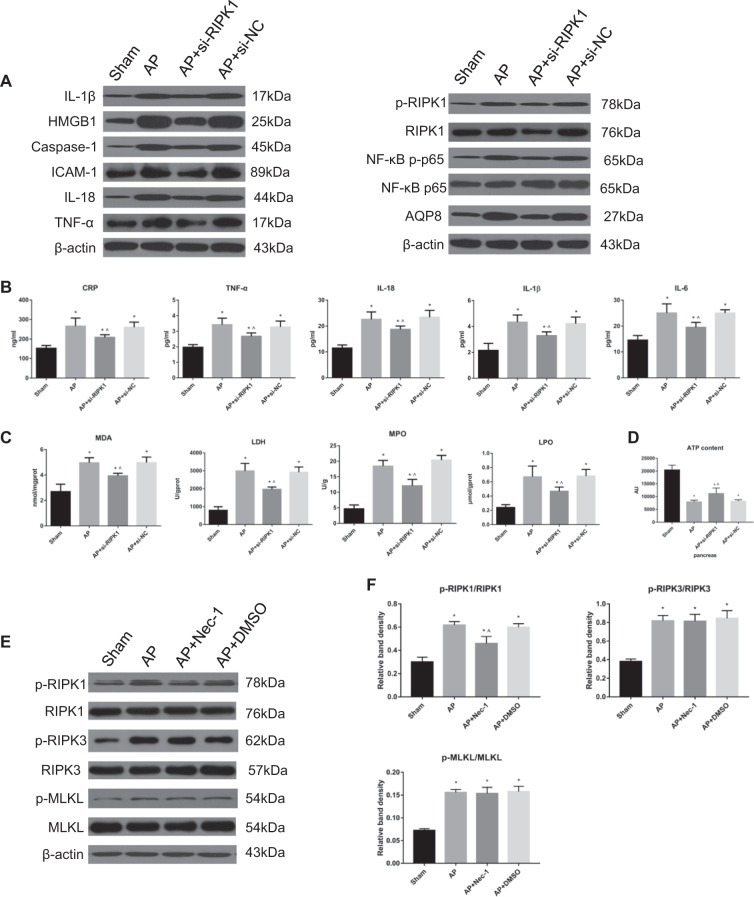
Fig. 4. Inhibition of RIPK1 did not affect the classic necroptosis pathway in AP rats.
a Representative immunoblot images and b quantitation of the IL-1β, HMGB1, Caspase-1, ICAM-1, IL-18, TNF-α, p-RIPK1/RIPK1, NF-κB p-p65/p65, and AQP8 levels in pancreatic tissues harvested from the rats described above in Fig. 3a. β-Actin was used as the protein loading control. b The levels of CRP, TNF-α, IL-18, IL-1β, and IL-6 in peripheral blood samples harvested from the rats described in Fig. 3a were spectrophotometrically measured. c The levels of MDA, LDH, MPO, and LPO in pancreatic tissues harvested from the rats described above in Fig. 3a were assessed spectrophotometrically. d The ATP levels in pancreatic tissues harvested from the rats in Fig. 3a were quantified. e Representative immunoblot images and f quantitation of the p-RIPK1/RIPK1, p-RIPK3/RIPK3, and p-MLKL/MLKL ratios in pancreatic tissues harvested from the rats described in Figure 3a. β-Actin was used as the protein loading control. The data are the means ± S.Ds. (n = 3). *P < 0.05 versus sham, ^P < 0.05 versus AP