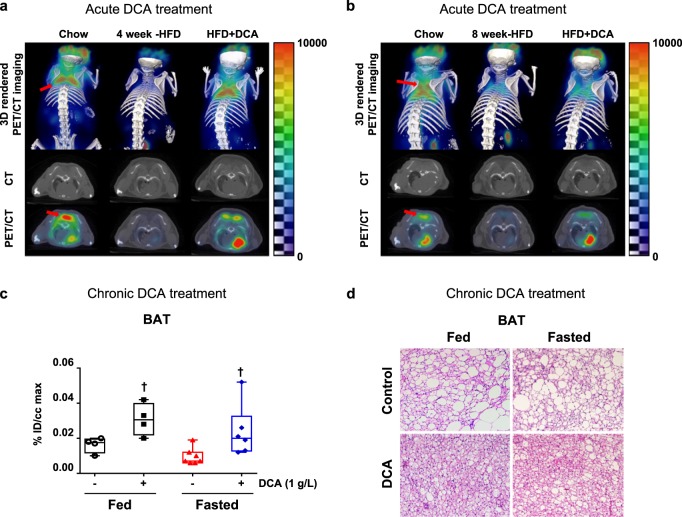
Fig. 4. Both the acute and chronic administration of DCA rescues HFD-induced BAT inactivation.
a, b 3D imaging and transverse imaging of 18F-FDG uptake in BAT after 4 (a) or 8 weeks (b) of HFD exposure. The BAT portion is indicated by the red arrow. c 18F-FDG uptake quantification in BAT after 14 weeks of HFD exposure, which included DCA (1 g/L) treatment via drinking water for the final 10 weeks (fed group, n = 4; fasted group, n = 6–7). d Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin staining of BAT after 14 weeks of HFD exposure, which included DCA (1 g/L) treatment via drinking water for the final 10 weeks (scale bar = 100 µm). The values are expressed as the mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed by Student’s t -test. †p < 0.05 vs. the WD-fed group