Fig. 6.
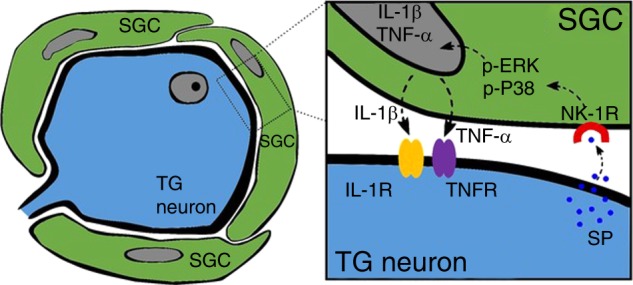
Schematic representation of a possible molecular mechanism involved in the effect of SP on the cytokine production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in TG SGCs. SP, secreted by TG neurons, causes SGC activation by activating NK-1 receptors expressed on the surface of SGCs, thus causing important downstream effects including upregulating the secretion of IL-1β and TNF-α by activating ERK and P38 MAPK pathways in SGCs. Then, IL-1β and TNF-α activate their specific receptors (IL-1R and TNFR) in TG neurons, resulting in enhanced cross-talk between TG neurons and SGCs, which plays an important role in inflammatory orofacial pain
