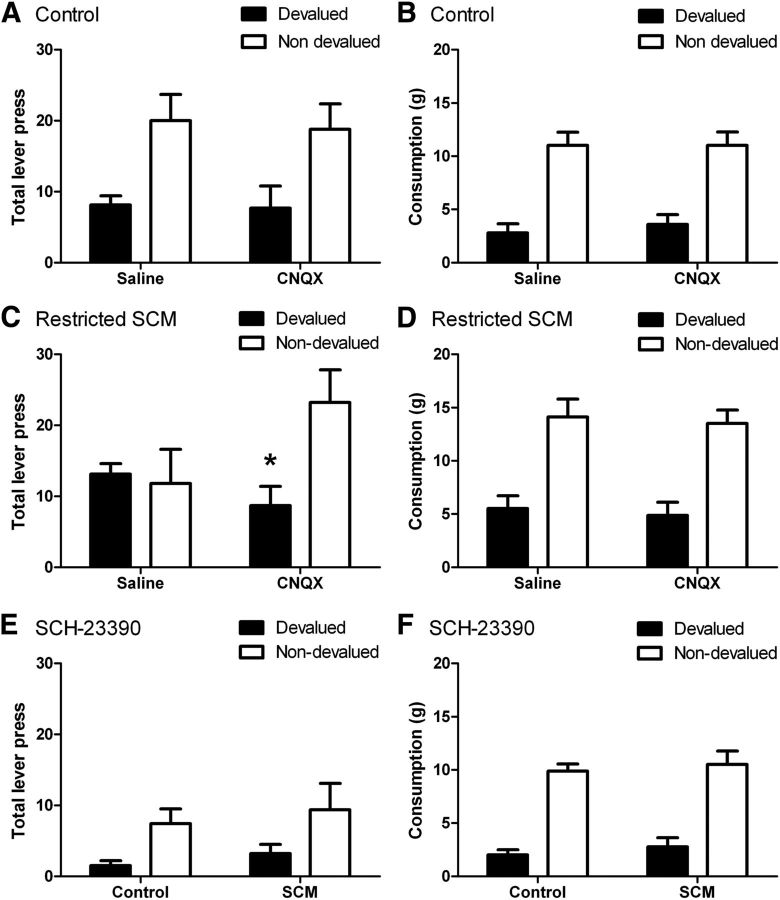
Figure 8.
Sensitivity to outcome devaluation following restricted access to a palatable food and effects of AMPA-receptor and D1-receptor antagonism in the DLS. A, C, Mean lever presses in a 5 min extinction test following prefeeding of the earned (devalued) or an alternative outcome (nondevalued) following infusions of either saline or CNQX. A, Control animals selectively decreased responding following devaluation and performance was unaffected by CNQX. C, Rats in the restricted-access group responded similarly regardless of devaluation condition, indicating loss of sensitivity to changes in outcome value following saline infusion. Infusion of CNQX restored sensitivity to devaluation in this group. Asterisk indicates p < 0.05. B, D, Consumption (in grams) of the same (devalued) or different (nondevalued) food consumed during the specific-satiety treatment for control (B) and SCM (D) groups. Both groups showed consumption that was sensitive to devaluation by specific satiety and ate less when given the same compared with a different food. E, F, Sensitivity to outcome devaluation following D1-receptor antagonism. Both groups showed similar sensitivity to devaluation following infusions of SCH-23390 measured in either lever-press performance (E) or consumption (F). N = 10 and 8 for the control and restricted-access groups, respectively.