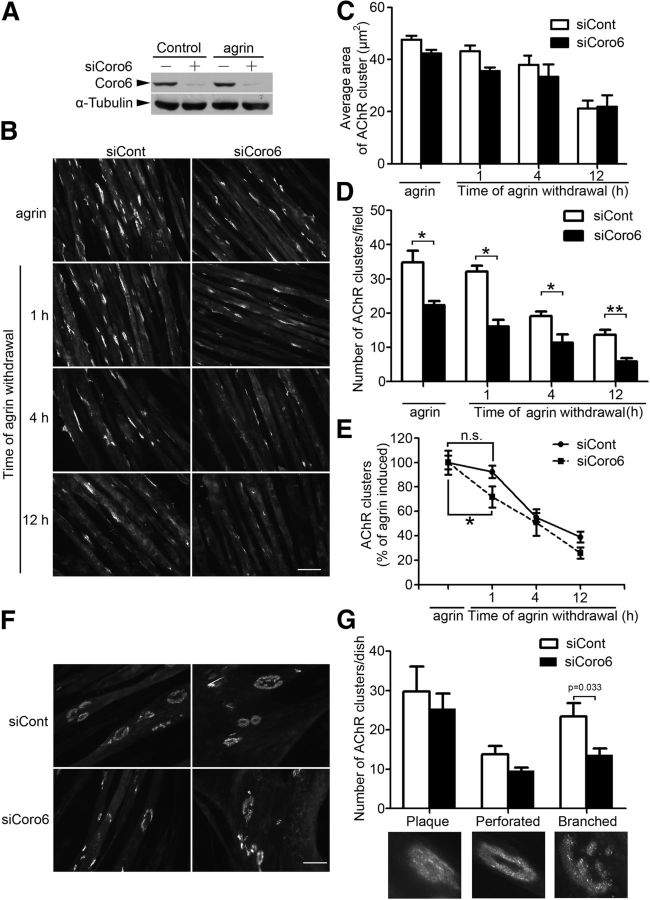
Figure 3.
Regulation of AChR clustering in myotubes by Coronin 6. A, C2C12 myotubes were transfected with siRNA against Coronin 6 (siCoro6) or luciferase as a control (siCont). Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies against Coronin 6 or α-tubulin. B–D, Coronin 6 regulates agrin-induced AChR clustering. C2C12 myotubes were transfected with siCoro6 or siCont followed by stimulation with agrin for 12 h to induce AChR clustering. For AChR dispersal, AChR clusters on agrin-treated myotubes were labeled with α-BTX. Myotubes were subsequently washed and maintained in agrin-free medium for an additional 1, 4, or 12 h. Representative images (B), and quantification of the size (C) and number (D) of AChR clusters on myotubes from each condition. The mean ± SEM of at least 3 experiments is indicated. *p < 0.05, siCoro6 versus siCont (Student's t test). **p < 0.01, siCoro6 versus siCont (Student's t test). Scale bar, 50 μm. E, The percentage of AChR clusters was calculated by normalizing the number of AChR clusters at different time points after agrin withdrawal to that at baseline. *p < 0.05, percentage of AChR clusters at the first hour of agrin withdrawal versus that at baseline in Coronin 6-silenced myotubes. n.s., Not significant. F, C2C12 myoblasts were cultured on laminin-coated plates and fused for 2 d, and the myotubes were subsequently transfected with siCoro6 or siCont. AChR clusters were visualized by AlexaFluor-555-conjugated α-BTX. Three types of AChR clusters are shown: plaque, perforated, and branched clusters. G, The numbers of each type of AChR cluster were counted from at least three individual experiments (branched clusters: siCont, 23.4 ± 3.4; siCoro6, 13.6 ± 1.6). p = 0.033, siCoro6 versus siCont (Student's t test).