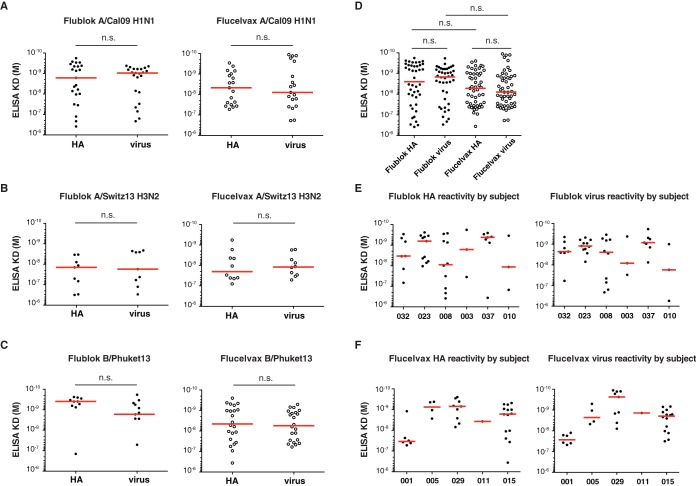
FIG 3.
Affinity of MAbs induced by Flublok or Flucelvax immunization. (A to F) Approximated KD values were determined for each MAb following binding to various rHAs and virus strains by ELISA. Each dot represents one MAb. Comparison of MAbs induced by Flublok or Flucelvax for binding against A/California/07/2009 H1N1 HA and virus, Flublok (n = 23) and Flucelvax (n = 19) (A); A/Switzerland/9715293/2013 H3N2 HA and virus, Flublok (n = 9) and Flucelvax (n = 10) (B); and B/Phuket/3073/2013 HA and virus, Flublok (n = 10) and Flucelvax (n = 22) (C). Cross-reactive MAbs that bound multiple strains were included in multiple comparisons. Statistical significance was determined by paired Wilcoxon test. n.s., not significant. (D) Comparison of all MAbs induced by Flublok or Flucelvax for binding against HA and virus. Statistical significance was determined by Mann-Whitney test for unpaired comparisons and Wilcoxon test for paired comparison. n.s., not significant. (E and F) Comparison of all MAbs induced by Flublok or Flucelvax for binding against HA and virus by subject.