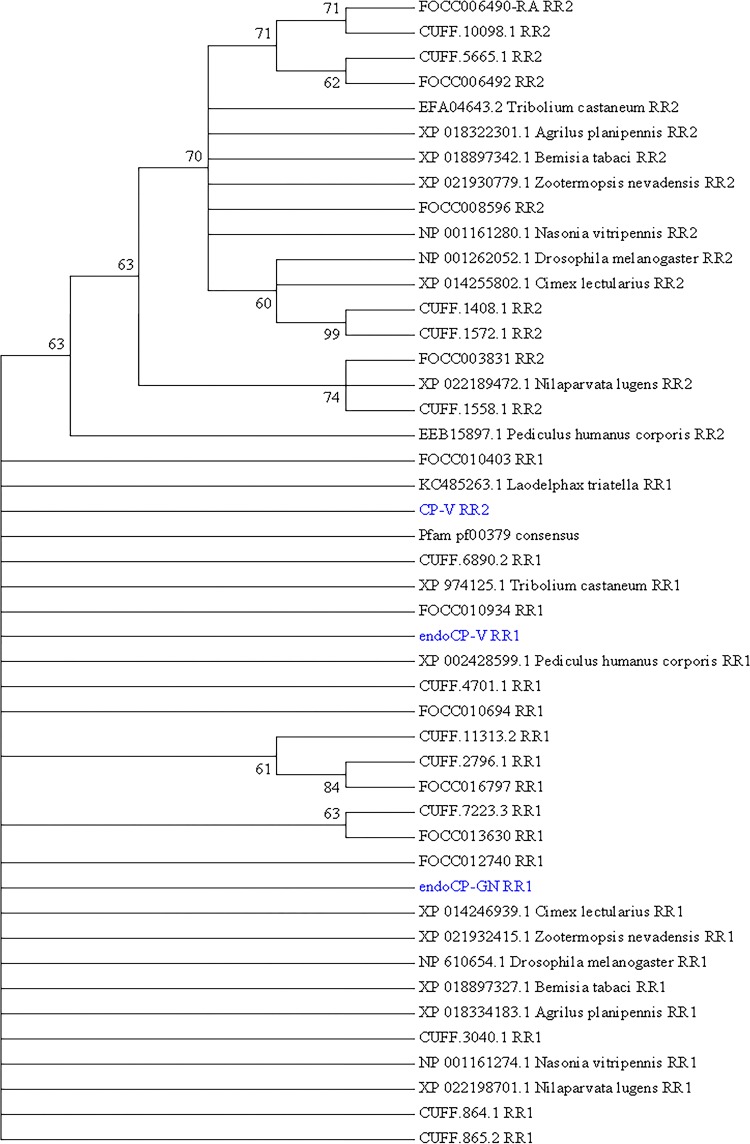
FIG 3.
Phylogenetic analysis of the extended R&R (Rebers and Riddiford, CPR-RR1 and CPR-RR2) consensus, a conserved chitin-binding motif (Chitin_bind_4 [CHB4]), of the three cuticle-associated TSWV-interacting proteins (TIPs) in first-instar larvae of Frankliniella occidentalis (cuticle protein-V [CP-V], endocuticle structural glycoprotein-V [endoCP-V], and endocuticle structural glycoprotein-GN [endoCP-GN]). The analysis involved 46 sequences, as follows: the three cuticle TIPs (in blue), the “gold standard” Pfam database extended R&R consensus sequence (pf00379), 19 insect orthologous sequences obtained from NCBI GenBank (accession numbers are present), and 23 structural CPs and endoCPs (translated transcripts, designated with FOCC or CUFF identifiers) previously reported to be differentially abundant in TSWV-infected first-instar larva of F. occidentalis (20). All positions with less than 30% site coverage in the multiple alignment were eliminated, resulting in 74 amino acid positions in the final data set. Evolutionary history was inferred by the maximum likelihood (ML) method based on the Jones-Taylor-Thornton (JTT) matrix-based model, and a discrete gamma distribution was used to model the variation among sites. The bootstrap consensus tree (500 replicates) was generated by the ML algorithm, and branches corresponding to partitions reproduced in less than 60% bootstrap replicates were collapsed. The numbers shown next to branches indicate the percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa (sequences) clustered together in the bootstrap test. The analysis was performed with MEGA7 (73).