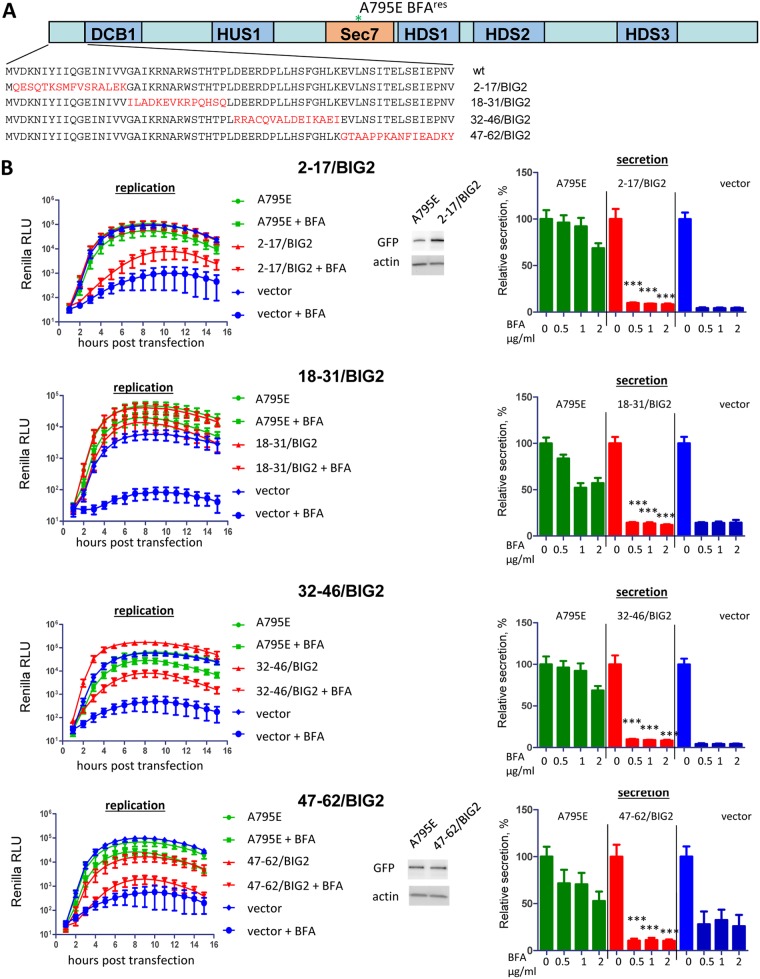
FIG 2.
Functional analysis of GBF1/BIG2 N-terminal chimeras in replication and secretion. (A) Scheme of the BIG2-derived substitutions in the GBF1 sequence. All GBF1 expression constructs are GFP tagged and contain the A795E BFA resistance mutation in the Sec7 domain. (B) Performance of the indicated mutants in the poliovirus replicon replication and cellular secretion assays. For the replication assay, cells were transfected with the plasmids expressing a corresponding GBF1 mutant, a full-length GBF1 A795E (positive control), or an empty vector (negative control). The next day, the cells were transfected with a poliovirus replicon RNA expressing Renilla luciferase and incubated in the presence or absence of 1 μg/ml BFA. Expression of the 2-17/BIG2 and 47-62/BIG2 constructs, the most compromised in the replication assay, is additionally verified by Western blotting in the samples from the corresponding experiments. For the secretion assay, the cells were cotransfected with plasmids coding for a corresponding GBF1 mutant, a full-length GBF1 A795E (positive control), or an empty vector (negative control) and a plasmid coding for a secreted Gaussia luciferase. The next day, they were washed and incubated in the medium with the indicated amount of BFA, and the amount of secreted luciferase was determined after 4 h. Secretion data are normalized to the signal obtained without BFA for each construct. The statistical significance of the difference between the signal in the positive control and that in the sample expressing a mutant GBF1 for corresponding concentrations of BFA is indicated.