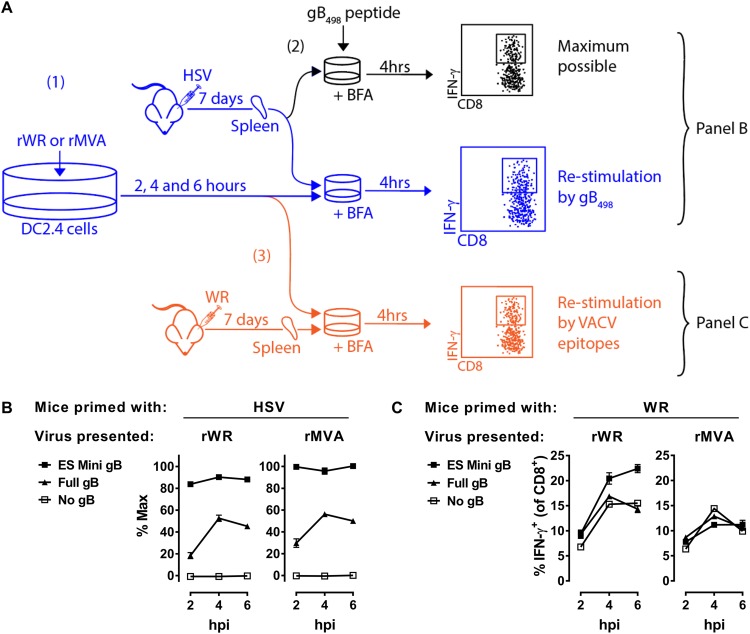
FIG 1.
Full-length gB and minigene-gB498 are expressed from rVACVs. (A) Diagram of experimental plan. DC2.4 cells were infected with rVACVs for 2, 4, or 6 h, and then the levels of HSV gB498 presentation on MHC-I were determined by coculture with HSV-immune splenocytes in the presence of brefeldin A, followed by flow cytometry to identify IFN-γ+ CD8+ T cells (blue, step 1). The HSV-immune splenocytes were separately stimulated with gB498 peptide for 4 h, and the percentages of CD8+ T cells that were IFN-γ+ were measured to provide a maximum possible gB498-specific response (black, step 2). Results from cocultures of infected cells with HSV-immune splenocytes are shown as a percentage of this maximum possible response. Finally, separate aliquots of the same infected cultures were incubated with VACV-immune splenocytes, and IFN-γ+ CD8+ T cells were again counted to determine the general levels of infection and antigen presentation (orange, step 3). (B) Data reflecting the levels of gB489 presented on triplicate cultures of rWR- or rMVA-infected cells from the experiment described above. The virus strain is shown above graphs, and the form of gB antigen expressed is in the key. (C) Data reflecting levels of VACV antigen presentation on the same triplicate cultures of rWR- and rMVA-infected cells. Means and standard errors of triplicates are shown; some errors are obscured by data points. The experiment was repeated with similar results.